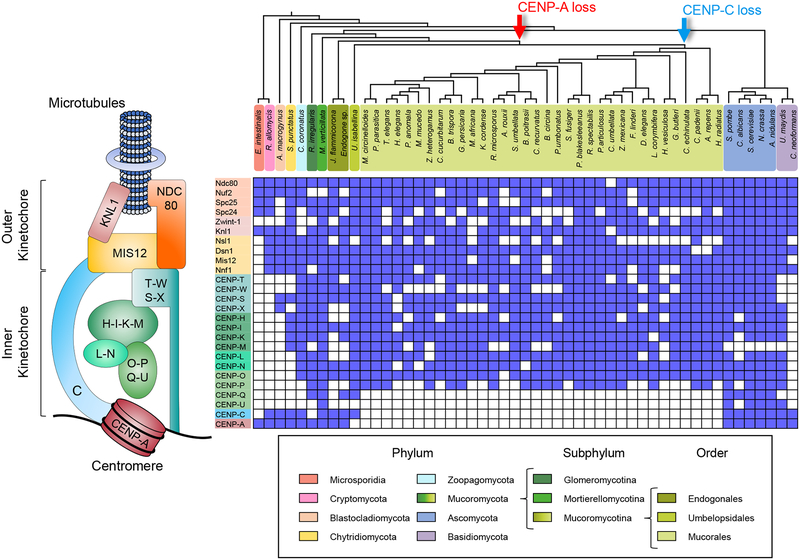
Figure 1. Distribution of the kinetochore complex across the Mucoromycotina subphylum.
Concise kinetochore schematic showing the most conserved protein in eukaryotes is shown on the left corresponding to the kinetochore proteins analyzed in matrix on the right. The matrix displays the presence or absence of 26 kinetochore across a cladogram of 51 fungal lineages (top) to show the relationships among them. fungal phylum is represented and color-coded, differentiating the Mucoromycota into Glomeromycotina, Mortierellomycotina, and Mucoromycotina subphyla to provide a emphasis on the latter. Arrows at divergence events in the cladogram mark the hypothetical loss of proteins CENP-A (red) and CENP-C (blue) in these clades. See also Figure S1, Tables S1 and S4.