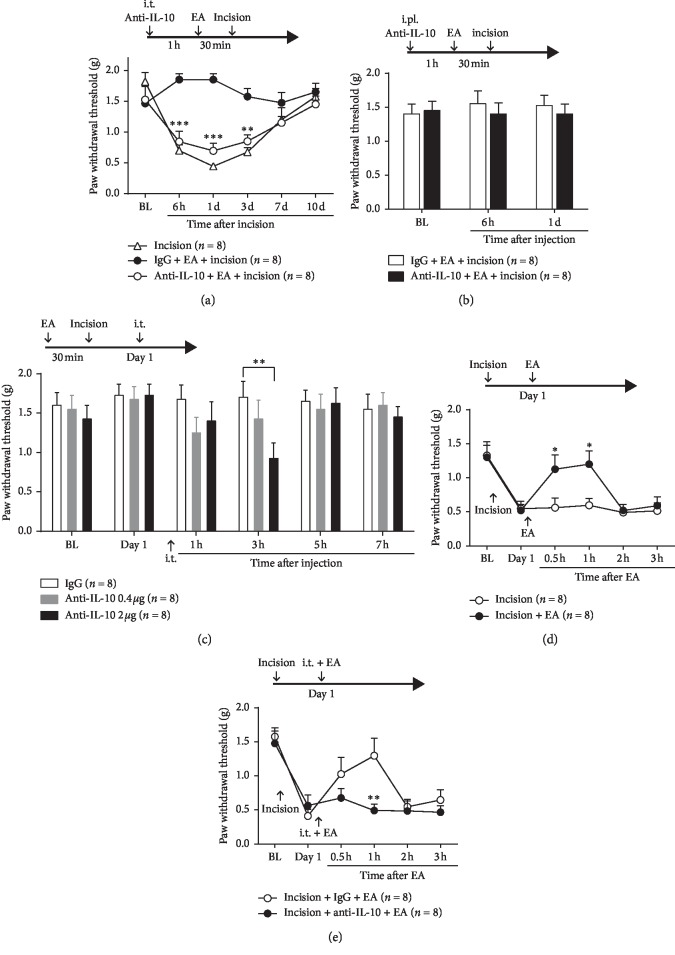
Figure 1.
Involvement of IL-10 in the analgesia of electroacupuncture (EA) on incision pain. (a) Incision-induced mechanical allodynia was blocked by EA (2/100 Hz, 1-2-3 mA, 30 min) and the analgesia effect of EA was reversed by lumbar puncture injection of anti-IL-10 neutralizing antibody (2 µg/10 µL) delivered 1 h before EA (P < 0.001, vs. IgG). (b) The analgesic effect of EA was not inhibited by intraplantar injection of anti-IL-10 antibody (10 µg/10 µL) 1 h before EA (P > 0.05, vs. IgG). (c) IL-10 neutralizing antibody (0.4 µg or 2 µg) was intrathecally injected on 1 d after incision and the ipsilateral PWTs were dose-dependently decreased at 3 h after injection compared with control IgG (P < 0.01, vs. IgG). (d) The incision-induced mechanical allodynia was relieved at 0.5 and 1 h after EA performed at 1 d after incision compared with the incision group (P < 0.01, vs. incision). (e) The analgesic effect at 1 h after EA was significantly blocked by intrathecal injection of IL-10 antibody 1 h before EA (P < 0.01, vs. IgG). ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001.