Figure 4.
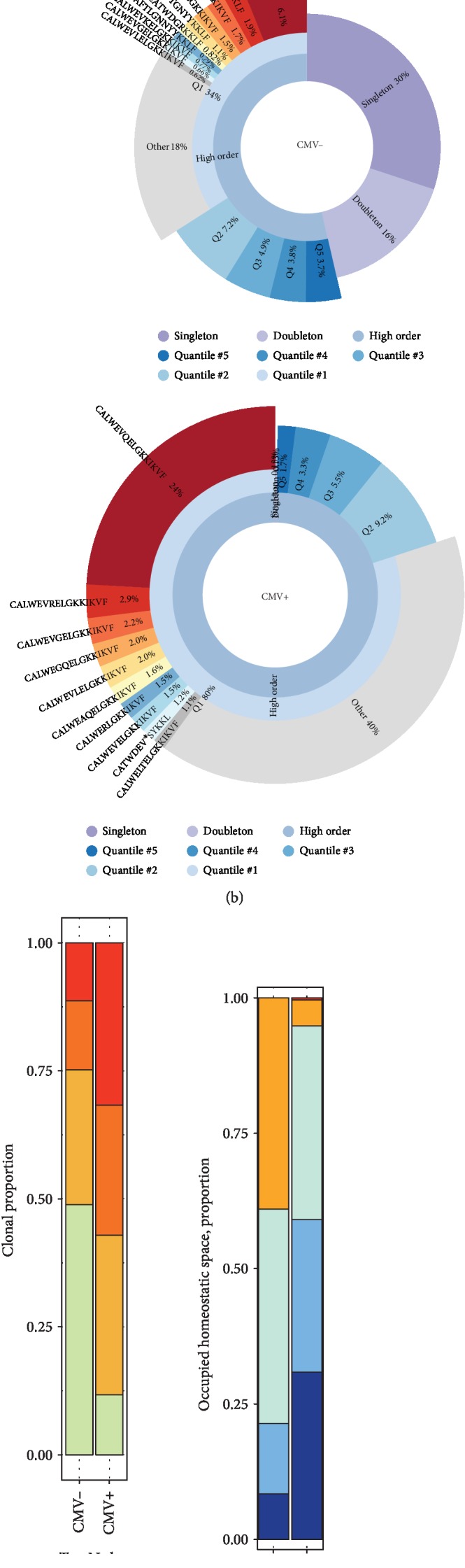
CMV+ BM grafts present less TRG diversity and high clonality. (a) Tree plots showing a CMV- and CMV+ BM graft donor TRG repertoire. Each CDR3 clonotype is colored accordingly to its amino acid sequence and is sized in relation to its repertoire frequency (the colors were chosen randomly and does not match between plots). (b) Quantile plots of a CMV- and CMV+ BM graft depicting the top 10 most frequent clonotypes. The pie chart is divided into singletons (clonotypes represented by a single read), doubletons (two reads), and high-order clonotypes (three and more reads). High-order clonotypes are divided into five quantiles (top 20% of unique high-order clonotypes and so on). The size of each segment is the cumulative frequency of all clonotypes that fall into the corresponding frequency category. (c) The clonal proportion of the top n clonotypes. Red bars represent the TRG proportion taken by the 10 most abundant clones shown in (b). (d) Proportion of homeostatic space occupied by clonotypes classified as hyperexpanded (0.01–1), large (0.001–0.01), medium (0.0001–0.001), small (0.00001–0.0001), and rare (0–0.00001).
