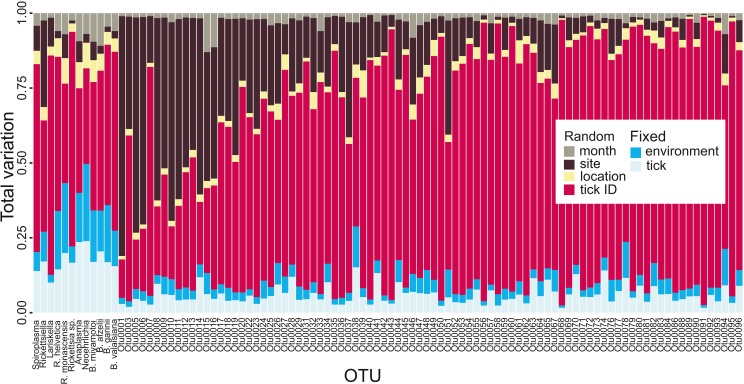
Figure 2. Tick microbial community variance partitioning for different fixed and random effects.
The first three columns represent tick endosymbionts, the next three columns are OTUs which are both tick endosymbionts and human pathogens and the subsequent six columns represent human pathogens. The other columns represent the 88 most common OTUs found in I. ricinus, ordered by read frequency. Month, sampling site, location and tick ID were included in the model as random effects, whereas fixed effects were divided into environmental (elevation, temperature, precipitation, forest coverage, slope, aspect, vole abundance and vole-to-other-rodents ratio) and tick-specific variables (life stage or sex, individual heterozygosity, abundance, expected population heterozygosity). See raw data in Figshare for information on OTU labels (DOI: 10.6084/m9.figshare.7380767.v3).