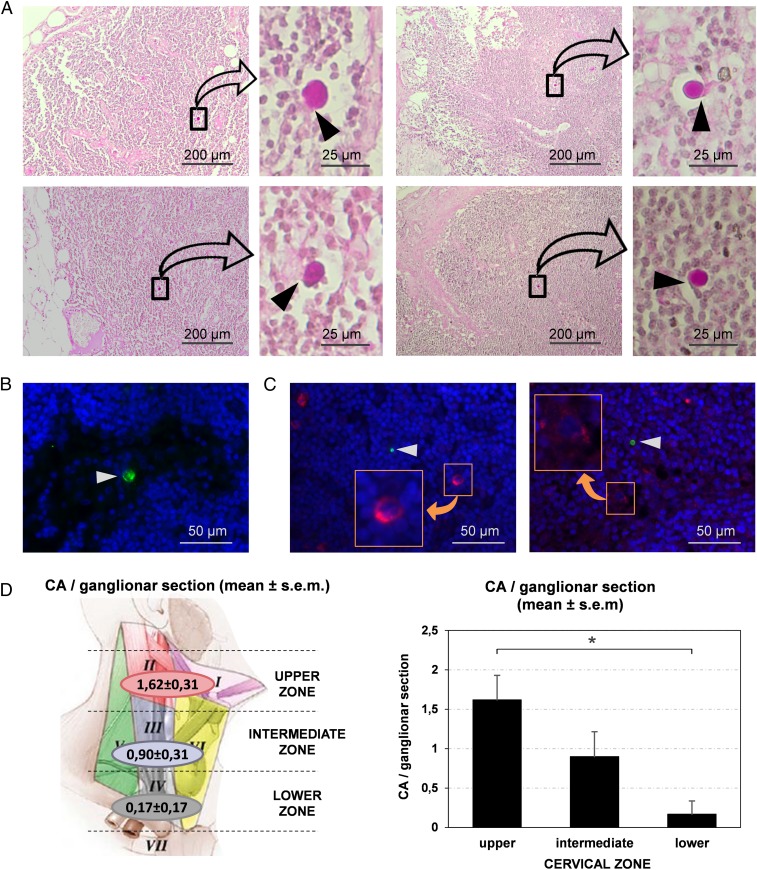
Fig. 4.
CA are present in the cervical lymph nodes. (A) Images of sections from different cervical nodes stained with PAS. For each section, a region containing CA is magnified. Note that CA exhibit specific contacts with some lymph node cells (arrowheads). (B) CA (arrowhead) can also be observed by immunofluorescence when sections are immunostained by IgMm α-NE (green). Blue staining (Hoechst) corresponds to the nuclei of lymph node cells. (C) Double staining with IgMm α-NE and α-FcµR (green and red respectively, Left image), and double staining with IgMm α-NE and α-CD35 (green and red respectively, Right image) indicate that some cells of the cervical lymph nodes contain FcµR and other cells express CD35 (Insets). However, the cells in contact with CA (arrowheads) did not stain with these antibodies. (D) Mean number (±SEM) of CA per section in the different regions of the neck. The upper region of the neck contains more CA per section than the lower one (P < 0.05), which suggests that brain CA reach the cervical lymph nodes, and that the nodes may retain or eliminate them.