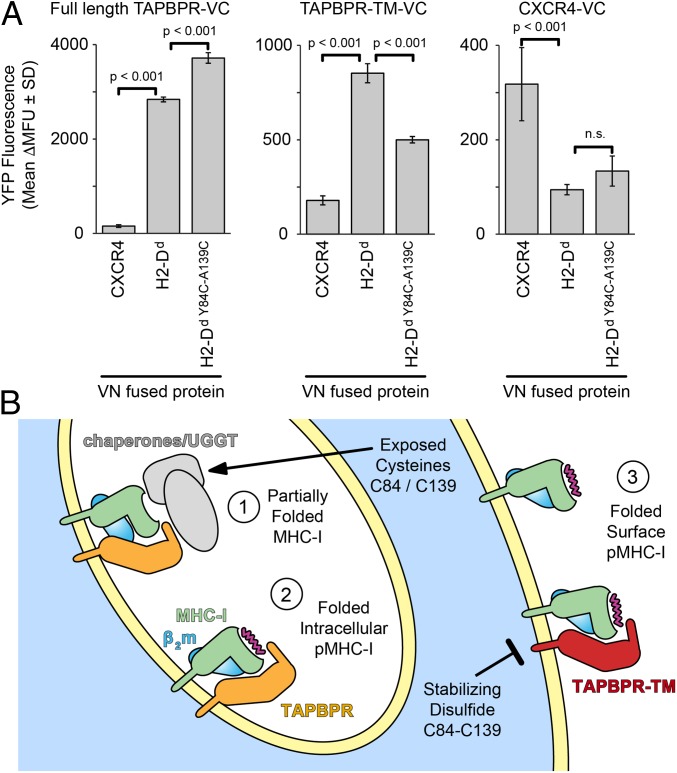
Fig. 6.
Restriction of MHC-I dynamics diminishes TAPBPR association on a cell membrane. (A) Cells were cotransfected with VC-fused FLAG-TAPBPR (Left), FLAG-TAPBPR-TM (Center), or FLAG-CXCR4 (Right), and with VN-fused myc-H2-Dd or myc-CXCR4. Yellow fluorescence (shown as average Δmean fluorescence units ± SD, n = 4) was measured after gating for equivalent expression levels. P values are calculated from 2-tailed Student’s t test. n.s., not significant. (B) Nascent MHC-I (step 1) within intracellular compartments associates with quality control machinery. The presence of additional, partially reduced cysteines is hypothesized to enhance chaperone associations, including direct or indirect recruitment of TAPBPR. As MHC-I completes its folding, it may transiently interact with TAPBPR (step 2) before mature pMHC-I traffics to the plasma membrane (step 3). The stabilizing disulfide diminishes direct interactions between folded pMHC-I molecules and TAPBPR.