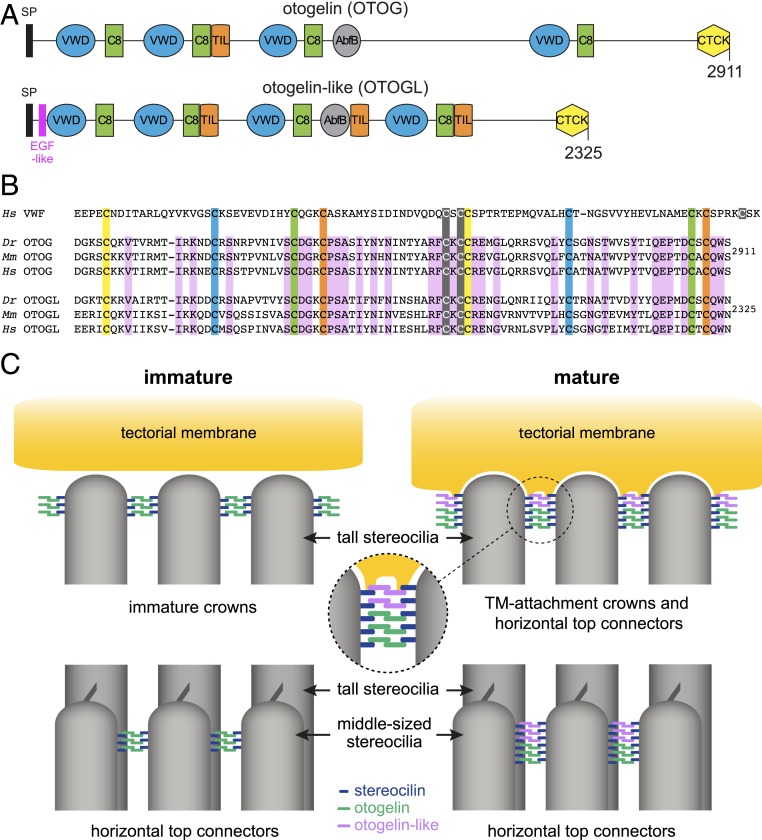
Fig. 9.
Otogelin and otogelin-like in the formation of TM-attachment crowns and horizontal top connectors in OHC hair bundles. (A) Modular structure of the mouse otogelin and otogelin-like proteins. SP, signal peptide; EGF-like, epidermal growth factor-like domain; VWD, von Willebrand factor-like domain; C8, cysteine-rich domain; TIL, trypsin inhibitor-like domain; AbfB, alpha-l-arabinofuranosidase B-like domain; CTCK, C-terminal cystine knot domain. (B) Comparison of the amino acid sequences of CTCK domains in the human (Homo sapiens; Hs) von Willebrand factor (vWF) and in the zebrafish (Danio rerio; Dr), mouse (Mus musculus; Mm), and human (Hs) otogelin (OTOG) and otogelin-like (OTOGL) proteins. According to the crystal structure of the vWF CTCK dimer (43), the 3 cysteine residues forming interchain disulfide bonds are highlighted in gray, and the 4 cysteine pairs forming disulfide bonds within each CTCK monomer are highlighted in yellow, blue, green, and orange. Amino acid residues conserved in the OTOG and OTOGL sequences of Dr, Mm, and Hs are highlighted in purple. (C) Proposed model for the formation of TM-attachment crowns and horizontal top connectors in immature and mature mouse OHCs. This model is based on the antiparallel homodimerization of otogelin and otogelin-like in the endoplasmic reticulum through the C-terminal cysteine knot domain, along with the close association of stereocilin with the plasma membrane. The interaction between stereocilin and otogelin or otogelin-like may be direct or indirect. The postnatal formation of the immature crowns initially involves stereocilin and otogelin, with the incorporation of otogelin-like at later stages. The first horizontal top connectors between the middle-sized stereocilia contain otogelin dimers bound to stereocilin. A few days later, new connectors contain otogelin-like dimers and stereocilin.