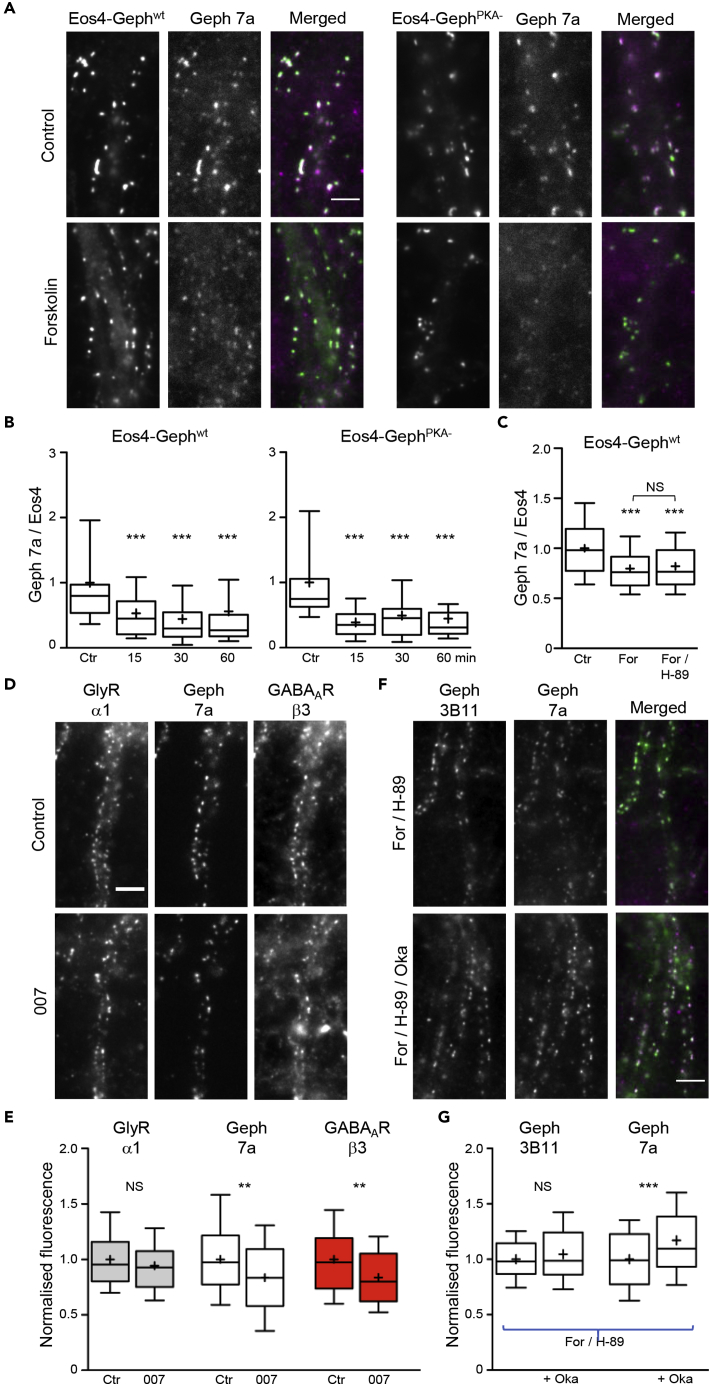
Figure 4.
PKA-Independent Effect of Forskolin on Gephyrin Phosphorylation
(A) mEos4b-tagged wild-type (wt) and PKA-insensitive (PKA-) gephyrin were expressed in rat spinal cord neurons using lentiviral infection (green in merged image). Cells treated without (Ctr) or with forskolin (For) were labeled with Geph 7a antibody (magenta) and GlyRα1 antibody (shown in Figures S1D and S1E). Scale bar, 5 μm.
(B) Time course of the ratio of Geph 7a/Eos4-Geph fluorescence intensity (normalized for each construct to the control condition in each experiment) after forskolin application of up to 60 min (n > 40 cells for each construct and time point from 2 experiments, ***p < 0.001 against control, KW test).
(C) After 30-min exposure to forskolin, the Geph 7a/Eos4-Geph ratio was consistently reduced, regardless of the presence of the PKA inhibitor H-89 (n = 60 cells per condition, 2 experiments, ***p < 0.001 against control, ANOVA).
(D) Triple immunostaining of GlyRα1, Geph 7a, and GABAARβ3 with or without the EPAC agonist 007 for 30 min. Scale bar, 5 μm.
(E) Normalized fluorescence intensity of 007-treated neurons (nCtr = 90, n007 = 83 cells from 3 experiments). EPAC activity significantly reduced Geph 7a and GABAARβ3 labeling, but not GlyRα1 (**p < 0.01, ANOVA).
(F and G) Spinal cord neurons were treated for 30 min with forskolin and H-89 in the presence or absence of 40 nM okadaic acid (Oka). Blockade of phosphatase PP1/PP2A increased the Geph 7a signal (magenta), but not Geph 3B11 (green), at the synapses (nFor/H89 = 86 and nFor/H89+Oka = 84 cells from 3 experiments, ***p < 0.001, t test). Scale bar, 5 μm. Data are represented as 10%, 25%, 50%, 75%, and 90% percentiles; the mean is indicated as a cross.