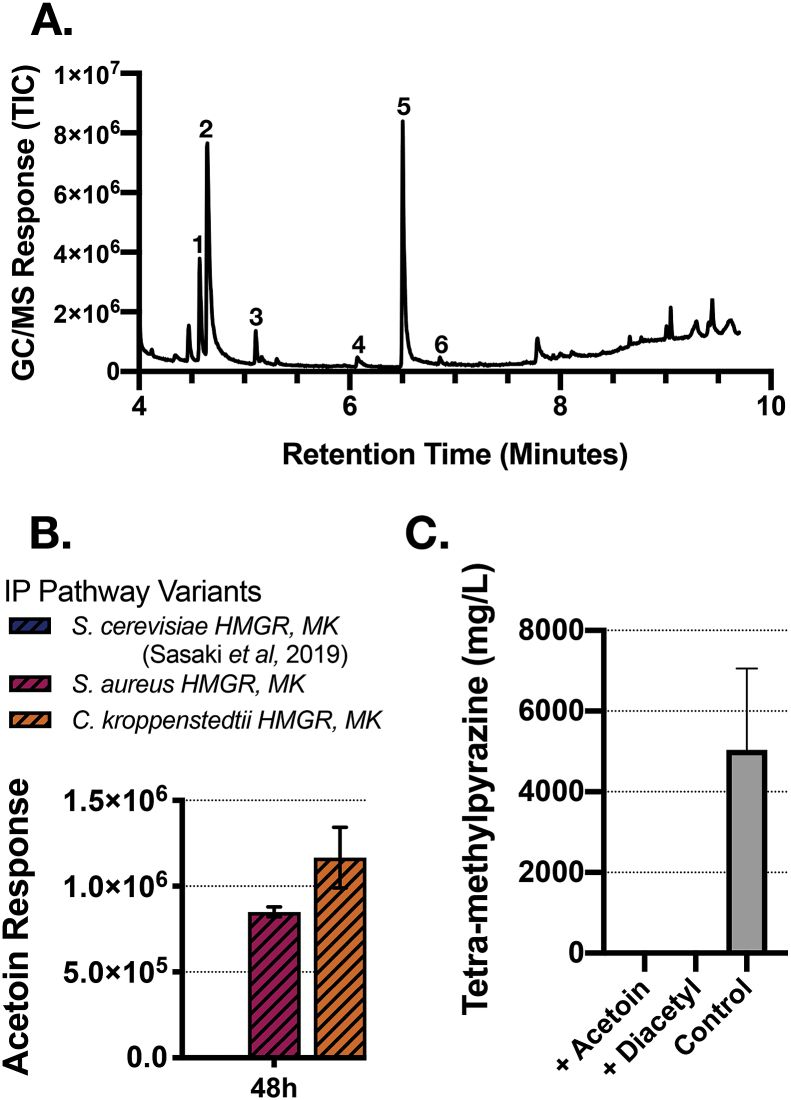
Fig. 4.
GC/MS analysis of tetra-methylpyrazine and S-acetoin. A. Identification of tetra-methylpyrazine and other peaks by GC/MS analysis. The genotypes of the strains used were the same as described in Fig. 2. Peak identification. 1. Acetoin (3-hydroxy-2-butanone). 2. Isopentenol (3-methyl-3-buten-1-ol). 3. 4-penten-1-ylacetate. 4. 2,3,5-tri-methyl-pyrazine. 5. 2,3,5,6-tetra-methyl-pyrazine. 6. 3,5-diethyl-2-methyl-pyrazine. B. Comparison of acetoin peak height across different engineered strains by GC/MS analysis. C. Detection of spontaneous TMP formation in CGXII media from precursors, acetoin or diacetyl, after 48 h post incubation. 100 mM of either acetoin or diacetyl was added to CGXII media. As a reference, TMP produced from the C. kroppenstedtii variant in JBEI-19658 is replotted from Fig. 2 on the same graph.