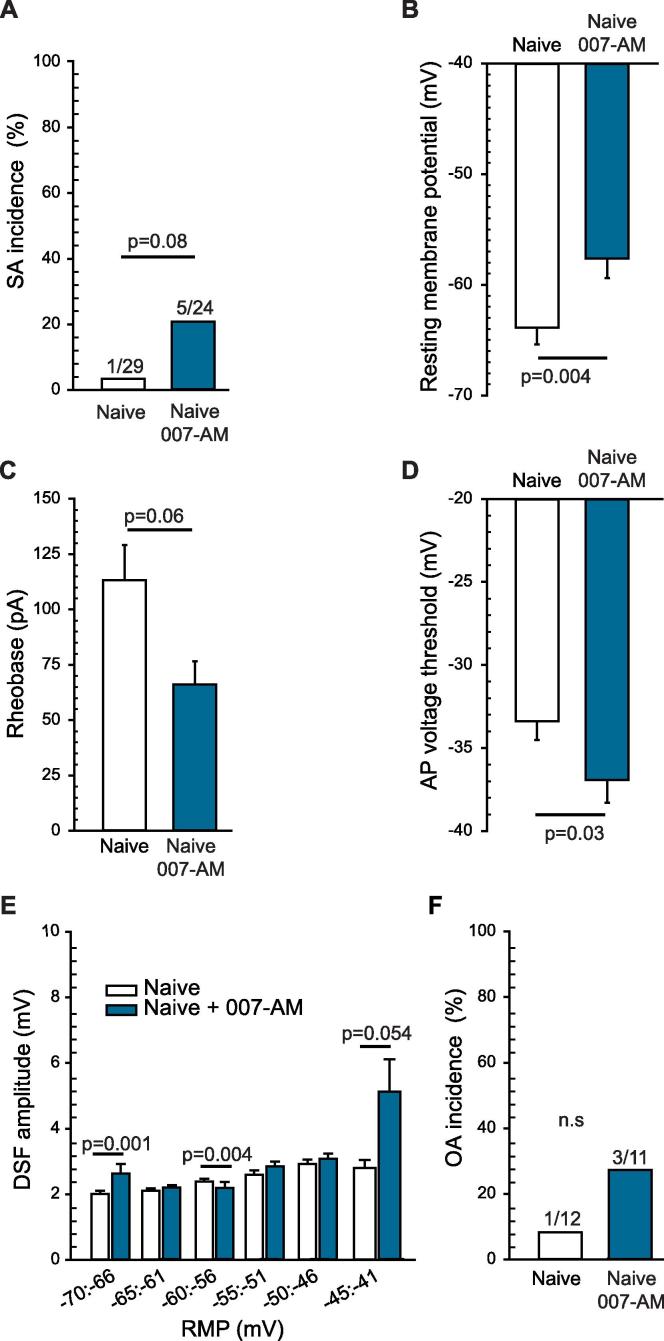
Fig. 2.
Activation of EPAC1 and 2 has a slight effect on DRG neurons isolated from naïve rats, depolarizing the RMP and hyperpolarizing AP voltage threshold. DRG neurons harvested from naïve rats were pretreated with 10 µM 8-pCPT-2-O-Me-cAMP-AM (007-AM) for 10–15 min before recording. (A) EPAC activation did not significantly affect SA incidence within neurons isolated from naïve rats. The ratio above each bar denotes the number of neurons with SA/the number of neurons sampled. Statistical comparison of SA was performed with Fisher’s exact test. (B) EPAC activation significantly depolarized RMP, with a trend toward a reduction in rheobase (C) and a significant hyperpolarization of AP voltage threshold. (D) Statistical comparisons of data (represented as mean ± SEM) were made by Mann Whitney U test. (E) EPAC activation significantly increased the DSF amplitudes at rest only for cells exhibiting RMP values between −45 and −41 mV. DSFs were binned according to initial voltage. Statistical comparison was performed by Kruskal-Wallis test followed by multiple comparisons with Dunn’s method for each duo of data at each bin of RMP. (F) EPAC activation did not significantly affect OA incidence. The ratio above each bar denotes the number of neurons with OA/the number of neurons sampled. Statistical comparison of OA was performed with Fisher’s exact test. DRG, dorsal root ganglion; DSF, depolarizing spontaneous fluctuation; EPAC, exchange protein activated by cAMP; n.s., non-significant; RMP, resting membrane potential; SA, spontaneous activity; SCI, spinal cord injury; SEM, standard error of the mean.