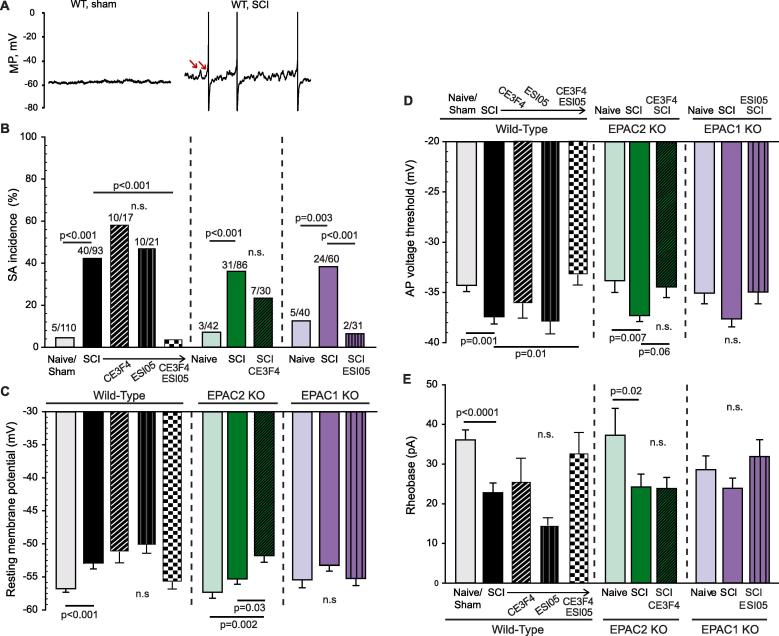
Fig. 4.
Inhibition of both EPAC1 and 2 isoforms is necessary to mitigate SCI-induced hyperexcitability in dissociated mouse DRG neurons. Small to medium-diameter DRG neurons (≤30 µm) harvested from lumbar levels were recorded by whole-cell patch clamp 18–30 h after dissociation. Neurons were pretreated with either vehicle, 10–20 µM CE3F4 or 5 µM ESI-05 for 15–20 min before recording. (A) Representative 10-second recordings obtained from neurons at RMP. Arrows indicate two of the larger DSFs. (B) Nociceptors isolated from EPAC1−/− or EPAC2−/− mice were not protected against increased incidence of SCI-induced SA; additional pharmacological inhibition of the complementary isoform was required to bring SA incidence towards a level comparable to neurons isolated from naïve/sham mice. The ratio above each bar denotes the number of neurons with SA/the number of neurons sampled. Statistical comparisons of SA incidence were made with Bonferroni-corrected Fisher’s exact tests on the indicated pairs. (C) SCI-induced depolarization of the RMP in wild-type and EPAC2−/− mice; additional inhibition of the EPAC1 isoform was required to mitigate SCI-induced depolarization within neurons isolated from EPAC2−/− mice. (D) SCI induced significant hyperpolarization of AP voltage threshold in wild-type and EPAC2−/− mice (trending within EPAC1−/− SCI mice); additional inhibition of the EPAC1 isoform did not cause a further significant change in the SCI-induced AP voltage threshold hyperpolarization within nociceptors from EPAC2−/− mice. (E) SCI decreased rheobase in wild-type and EPAC2−/− mice (trending within EPAC1−/− SCI mice); additional inhibition of the EPAC1 isoform did not cause a further significant change in the SCI-induced decrease in rheobase within nociceptors from EPAC2−/− mice. Comparisons of data (mean ± SEM) were made by t-test (for wild-type data), or Kruskal-Wallis followed by Dunn’s method for pairwise comparisons AP, action potential; DRG, dorsal root ganglion; EPAC, exchange protein activated by cAMP; KO, knock-out; MP, membrane potential; NA, nonaccommodating; n.s., non-significant; SA, spontaneous activity; SCI, spinal cord injury; SEM, standard error of the mean; WT, wild-type.