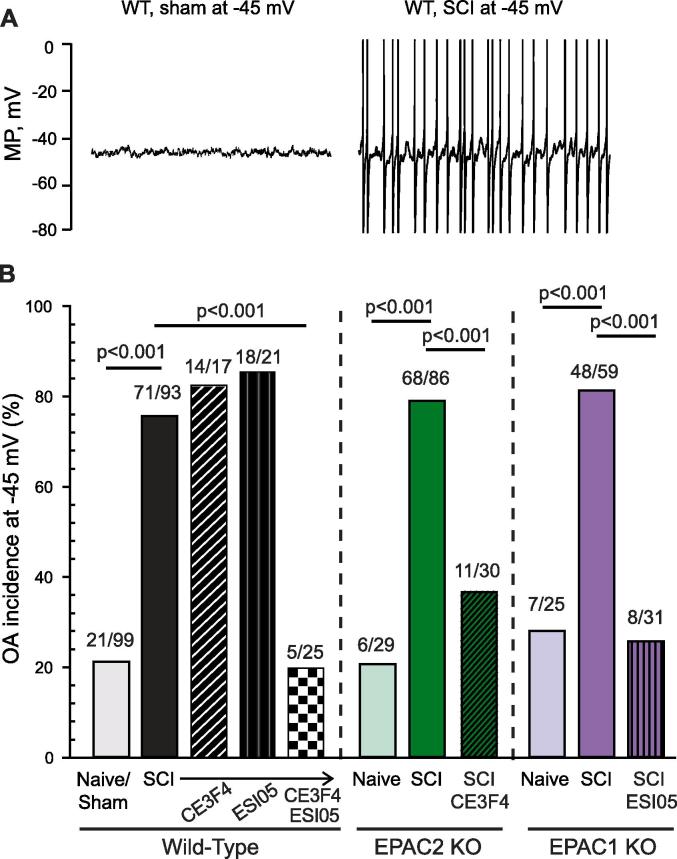
Fig. 6.
Inhibition of both EPAC1 and 2 is necessary to mitigate SCI-induced OA in presumptive mouse nociceptors. To measure extrinsically driven OA, small DRG neurons were artificially depolarized to −45 mV by current injection for 30–60 s. DRG neurons isolated from EPAC1−/− or EPAC2−/− mice were not protected against SCI-induced OA; additional inhibition of the complementary isoform was required to reverse the effect of the injury. (A) Representative 10-second recordings obtained from neurons artificially held at −45 mV. APs are clipped at 0 mV to allow sufficient magnification for clear display of DSFs. (B) Incidence of OA measured at a holding potential of −45 mV. The ratio above each bar denotes the number of neurons with OA/the number of neurons sampled. Statistical comparisons of OA incidence were made with Bonferroni-corrected Fisher’s exact tests on the indicated pairs. DRG, dorsal root ganglion; EPAC, exchange protein activated by cAMP; KO, knock-out; OA, ongoing activity; MP, membrane potential; SCI, spinal cord injury; WT, wild-type.