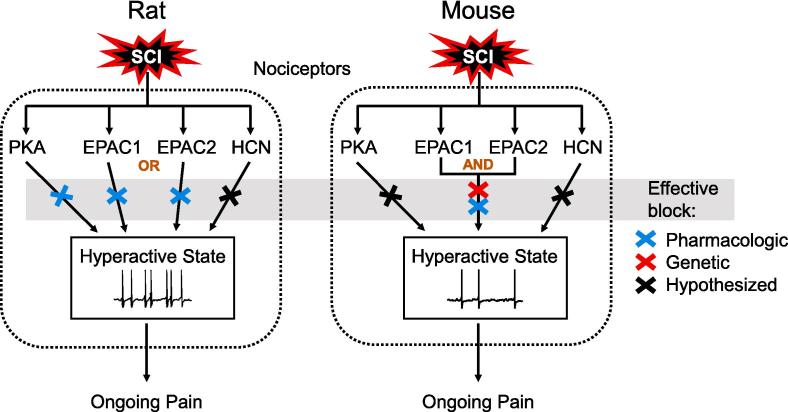
Fig. 8.
Comparison of the contributions of cAMP effectors in rat and mouse nociceptors to the maintenance of SCI-induced hyperactivity (SA and OA) and links to ongoing pain. In rat nociceptors, pharmacological inhibition (blue x's) of either EPAC isoform is sufficient to block the hyperactivity. In mouse nociceptors, block of both EPAC isoforms is necessary to block the hyperactivity, either by combining two EPAC inhibitors or an inhibitor for one isoform with genetic deletion of the second isoform (red x). The necessity of PKA in rat nociceptors for hyperactivity after SCI was reported previously (Bavencoffe et al., 2016), while the necessity of HCN channels for similar hyperexcitability has been reported in other injury models (Bernal and Roza, 2018, Djouhri et al., 2015, Djouhri et al., 2018, Emery et al., 2011, Young et al., 2014) and observed after SCI (A.G. Bavencoffe, C.W. Dessauer and E.T. Walters, unpublished observations). (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)