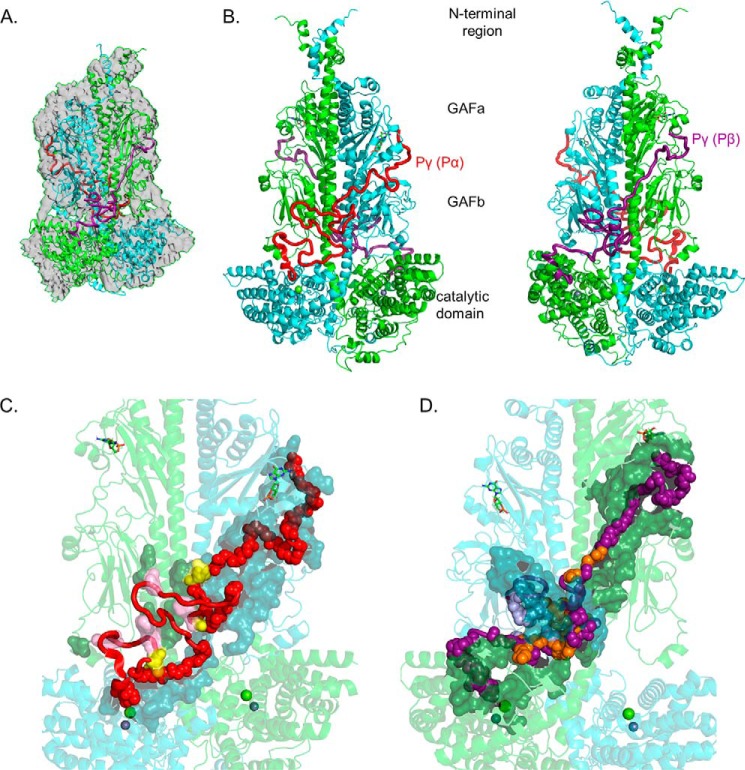
Figure 1.
Integrative structural model of the PDE6 holoenzyme. The structural model of rod PDE6 holoenzyme (αβγγ) was determined by using the cryo-EM structure 6MZB (23) as a template and applying spatial restraints determined by chemical cross-linking of purified bovine rod PDE6 (Table 1 and Ref. 20). In the model, PDE6 subunits are colored as follows: α-subunit (Pα), cyan; β-subunit (Pβ), green; Pγ subunit primarily associated with α-subunit (Pγ(Pα)), red; and Pγ subunit primarily associated with β-subunit (Pγ(Pβ)), deep purple. A, superimposition of the template cryo-EM map (EMD-9297) with the cross-link–refined structural model of nonactivated PDE6 holoenzyme. B, asymmetric interactions of Pγ with the Pαβ catalytic dimer extending from the cGMP-binding GAFa domain to the GAFb domain and then crossing over to the catalytic domain to the site of inhibition of catalysis. Each Pγ subunit primarily interacts with one catalytic subunit. The two images are rotated 180°. C, interaction surface of the Pγ(Pα) subunit with the PDE6 catalytic dimer. Pγ(Pα) residues interacting with the catalytic dimer are shown as main-chain atom spheres: red, residues interacting with the α-subunit; pink, residues interacting with the β-subunit; and yellow, Pγ residues that interact with both catalytic subunits. Noninteracting Pγ(Pα) residues are shown as red loops and α-helix. The catalytic subunit interacting residues are shown as a surface representation (α-subunit, dark cyan; β-subunit, dark green). D, interaction surface of the Pγ(Pβ) subunit with Pαβ. The interaction surface of the Pγ(Pβ) subunit (180° rotation in C) is depicted in which the deep purple, light purple, and orange spheres represent interactions with the β-subunit, α-subunit, or both catalytic subunits, respectively.