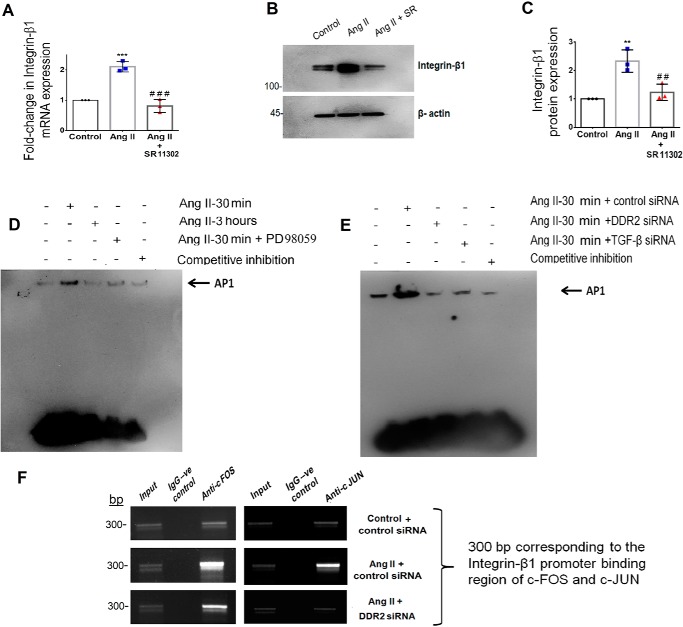
Figure 2.
Transcriptional regulation of integrin-β1 by AP-1 via DDR2-dependent ERK1/2 MAPK/TGF-β1 signaling in Ang II–stimulated cardiac fibroblasts. A, subconfluent quiescent cultures of cardiac fibroblasts were pretreated with AP-1 inhibitor (SR11302) for 1 h and, subsequently, with Ang II. integrin-β1 mRNA levels were determined by RT-qPCR analysis at 6 h of Ang II treatment. β-Actin served as the endogenous control. ***, p < 0.001 versus control; ###, p < 0.001 versus Ang II. B and C, protein was isolated at 12 h post-Ang II treatment and subjected to Western blot analysis for detection of integrin-β1, with β-actin as loading control. **, p < 0.01 versus control; ##, p < 0.01 versus Ang II. D, EMSA was performed as described under “Experimental procedures.” Ang II enhanced AP-1 nuclear translocation at 30 min post-treatment, which was attenuated at 3 h. ERK1/2 MAPK inhibition using PD98059 reduced Ang II–induced AP-1 activation at 30 min. E, Ang II enhanced AP-1 nuclear translocation at 30 min post-treatment, which was attenuated upon siRNA-mediated silencing of DDR2 and TGF-β1, respectively. F, DNA binding of AP-1 subunits, c-Fos and c-Jun, to the integrin-β1 (ITGB1) gene promoter was confirmed by ChIP using anti-c-Fos and anti-c-Jun antibody, respectively. A nonspecific anti-rabbit IgG was used as negative control. A representative image showing the PCR amplification product is given. Data are representative of three independent experiments (n = 3). Error bars, S.D.