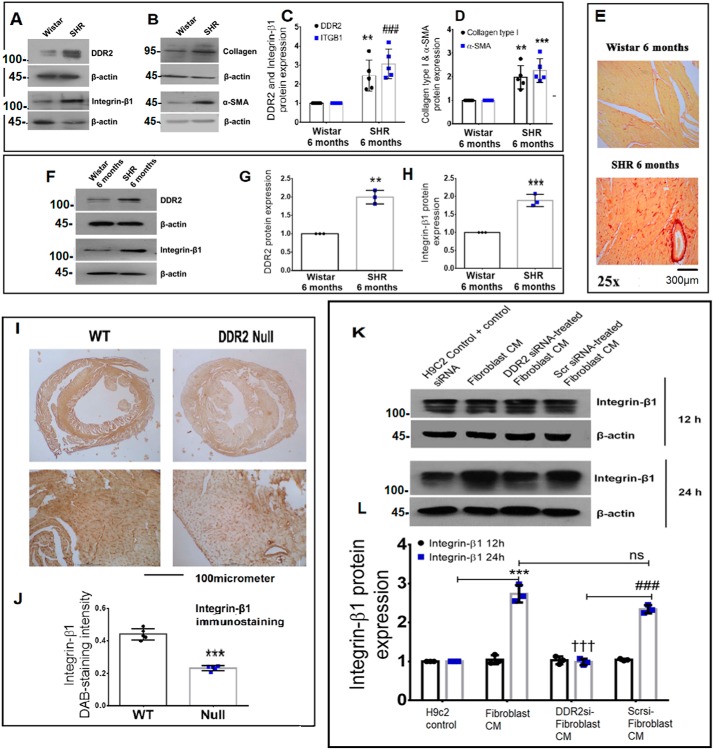
Figure 3.
Corroboration of the DDR2–integrin-β1 link in vivo. A–D, cardiac tissues of 6-month-old Wistar rats and SHRs were probed for DDR2, integrin-β1, collagen α1(I), and α-SMA expression by Western blot analysis. **, p < 0.01 versus Wistar for DDR2. ###, p < 0.001 versus Wistar for integrin-β1 (ITGB1). **, p < 0.01 versus Wistar for collagen α1(I). ***, p < 0.001 versus Wistar for α-SMA (n = 5). E, cardiac tissue sections of 6-month-old Wistar rats and SHRs were stained for collagen using picrosirius red (×25 magnification) (n = 4). F–H, cardiac fibroblasts were isolated from 6-month-old Wistar rats and SHRs. The cells were preplated for 2.5 h followed by protein isolation and subjected to Western blot analysis for detection of DDR2 and integrin-β1, with β-actin as loading control. **, p < 0.01 versus Wistar for DDR2; ***, p < 0.001 versus Wistar for integrin-β1 (n = 3). I and J, 3,3′-diaminobenzidine (DAB) staining showing integrin-β1 protein in myocardial tissue sections of 10-week-old WT and DDR2-null mice. ***, p < 0.001 versus WT (n = 5). K and L, subconfluent quiescent cultures of rat ventricular H9c2 cells were treated with conditioned medium (CM) derived from control rat cardiac fibroblasts or DDR2-silenced rat cardiac fibroblasts or control siRNA-treated rat cardiac fibroblasts for 12 or 24 h. Quiescent cultures of H9c2 in M199 without serum were used as control for basal integrin-β1 protein expression in H9c2 cells. Integrin-β1 protein expression in H9c2 cells was examined by Western blot analysis and normalized to β-actin. ***, p < 0.001 versus H9c2 control at 24 h; †††, p < 0.001 versus fibroblast CM at 24 h; ###, p < 0.001 versus DDR2 siRNA–treated fibroblast CM at 24 h; ns, not significant. Three rats (Sprague–Dawley) were used for cardiac fibroblast isolation for the conditioned medium experiments (n = 3). Error bars, S.D.