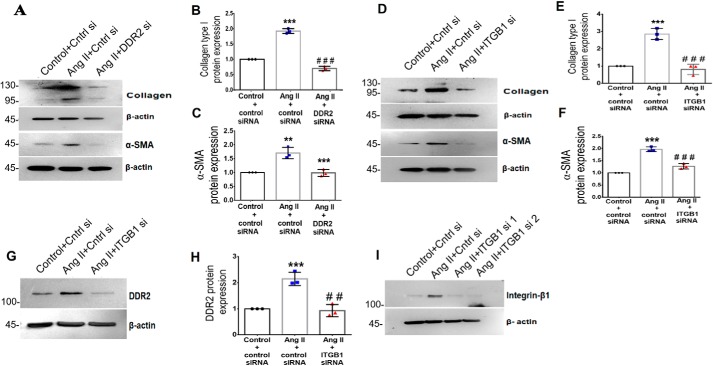
Figure 4.
Ang II–induced integrin-β1 regulates DDR2, α-SMA, and collagen type I expression in cardiac fibroblasts. A–C, cardiac fibroblasts were transiently transfected with DDR2 siRNA or scrambled siRNA (control). Following exposure of the transfected cells to Ang II for 12 h, collagen α1(I) and α-SMA protein levels were analyzed, with β-actin as loading control. ***, p < 0.001 versus control; ###, p < 0.001 versus Ang II for collagen α1(I). **, p < 0.01 versus control; ***, p < 0.001 versus Ang II for α-SMA. D–F, cardiac fibroblasts were transiently transfected with integrin-β1 (ITGB1) siRNA or scrambled siRNA (control). Following exposure of the transfected cells to Ang II for 12 h, collagen α1(I) and α-SMA protein levels were analyzed, with β-actin as loading control. ***, p < 0.001 versus control; ###, p < 0.001 versus Ang II. G and H, cardiac fibroblasts were transiently transfected with integrin-β1 (ITGB1) siRNA or scrambled siRNA (control). Following exposure of the transfected cells to Ang II for 12 h, DDR2 protein expression was examined by Western blot analysis and normalized to β-actin. ***, p < 0.001 versus control; ##, p < 0.01 versus Ang II. I, representative image of integrin-β1 siRNA validation. Knockdown efficiency of integrin-β1 siRNA1 or siRNA2 on integrin-β1 protein expression was checked. siRNA2 was used for silencing integrin-β1. Data are representative of three independent experiments (n = 3). Error bars, S.D.