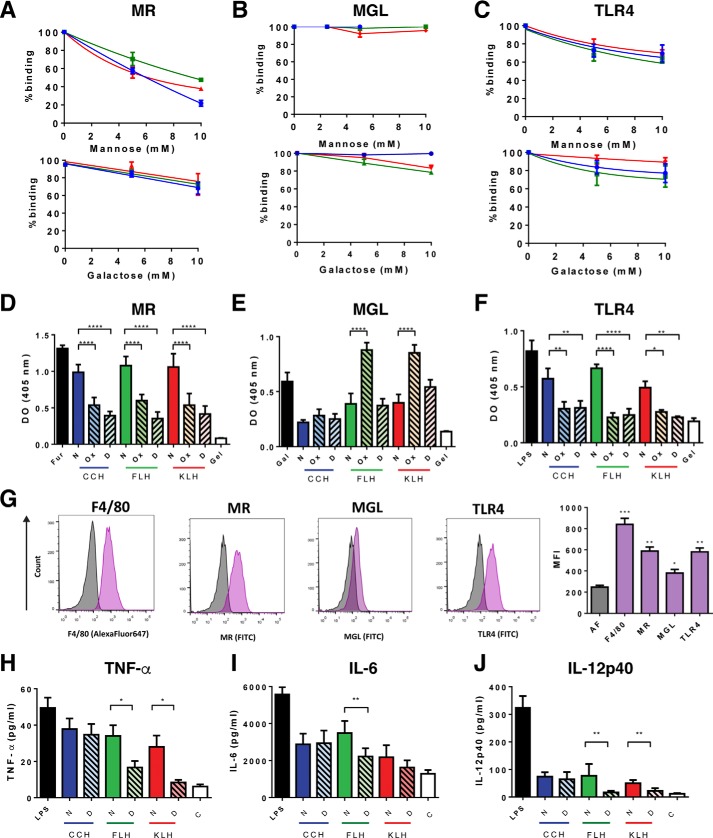
Figure 4.
N-Glycans promoted hemocyanin binding to chimeric innate immune receptors and cytokine secretion in J774.2 macrophages. Competitive hemocyanin binding to chimeric TLR4-Fc (A), MR-Fc (B), and MGL-Fc (C) in the presence of glycans, analyzed by ELISA. Chimeric receptors (1 μg/ml) were incubated with d-(+)-mannose or d-(+)-galactose (0–100 mm) and then with native hemocyanins (2.5 μg/ml). The binding was revealed with anti-Fc antibodies (goat anti-human Fc-FAL or goat anti-mouse Fc-FAL serum). D–F, reactivity of chimeric receptors with native (N), chemically deglycosylated (Ox), and N-deglycosylated (D) hemocyanins by ELISA. Hemocyanins (2.5 μg/ml) were incubated with the chimeric receptors (1 μg/ml) and with anti-Fc antibodies. Furfurman (Fur), lipopolysaccharide from E. coli (LPS), and d-(+)-galactose (Gal) were used as positive controls, and gelatin (Gel) was the negative control. G, analysis of innate immune receptors in J774.2 cells by flow cytometry. J774.2 cells were incubated with an anti-F4/80–Alexa Fluor-647 antibody, as well as primary anti-MR, anti-TLR-4, and anti-MGL following goat anti-rat IgG–FITC serum. Representative histograms of autofluorescence (gray) and the expression of the different markers (purple), as well as the quantification of the MFI are shown, including the autofluorescence signal (AF). Analysis of cytokine expression in J774.2 cells by ELISA. TNFα (H), IL-6 (I), and IL-12p40 (J) from J774.2 culture supernatants were quantified by ELISA after 24 h of incubation with native (N) and N-deglycosylated (D) hemocyanins. LPS from E. coli and the culture medium without hemocyanin (C) were used as positive and negative controls, respectively. For all experiments, the data are shown as the mean ± S.E. of three independent experiments. Analyses were done by t test. *, p < 0.5; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001.