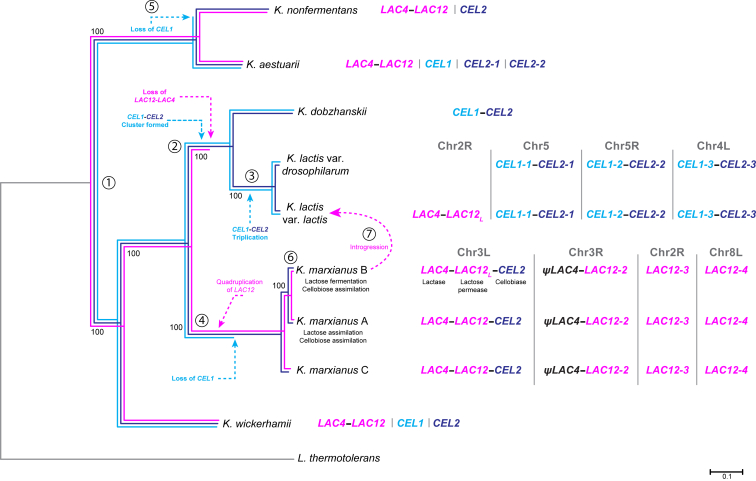
Figure 1.
Summary of Evolutionary Steps in Lactose and Cellobiose Utilization in the Genus Kluyveromyces
Colored branches on the phylogenetic tree trace the history of the LAC4-LAC12 gene cluster (magenta), CEL1 (cyan), and CEL2 (dark blue). Dashed arrows mark key evolutionary steps, including gene duplications, losses, and relocations. Numbers refer to specific events that are discussed in the main text. The dashed magenta arrow shows the introgression of the LAC12L gene and the neighboring LAC4 from a K. marxianus haplotype B strain into a lactose negative progenitor of K. lactis var. lactis, leading to the modern species that is now able to assimilate and ferment lactose. The LAC and CEL genotype is shown for every species. The chromosome numbers for the K. lactis species refers to chromosomes in K. lactis var. lactis CBS2359. Dashes between gene names indicate genes that are clustered in the genome.