Figure 2.
Reducing tam Gene Dose Increased the Abundance of Functional mtDNA in Two Heteroplasmic Lines
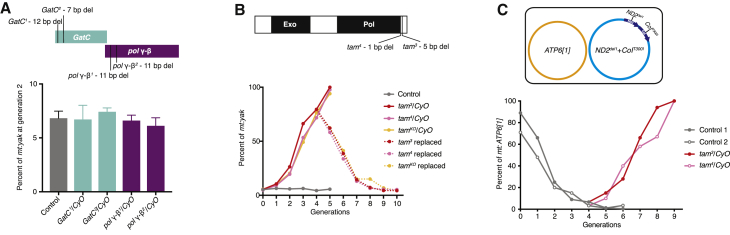
(A) Reducing the dose of pol γ-β or GatC showed no effect on mtDNA competition. Top: a schematic shows the genomic arrangement of the co-transcribed genes GatC and pol γ-β with the position and description of loss-of-function mutants isolated via CRISPR/Cas9-based editing (Figure S2). Bottom: the histogram shows the mt:yak percentage for different nuclear genotypes. Error bars indicate SDs of three independent experiments.
(B) Heterozygosity for any of the three mutant alleles of tam over the CyO chromosome dramatically shifted the heteroplasmic ratio (see Figure S3 for the total mtDNA copy number of the tam heterozygotes). Top: a schematic of Tam protein shows functional domains and the positions of two homozygous lethal mutations, tam3 and tam4. At 29°C, the mt:yak percentage increased in tam3, tam4, and tamKO heterozygous mutants with a speed similar to that observed with the BSC252 and BSC812 deficiencies (Figure 1C). Chromosomes bearing tam mutations were introduced at generation 0 and the mt:yak percentage was followed over generations via qPCR (solid line). From generation 1 to 3, only progeny heterozygous for the tam mutation were followed and crossed to KrIf/CyO to examine the cross-generational dose effect of tam. At generation 4, the female progeny lacking the tam mutation were also mated with KrIf/CyO, and these populations were maintained in parallel for another 6 generations to assess the mt:yak percentage (dotted lines).
(C) Reducing tam dose also increased the percentage of the functional genome (mt:ATP6[1]) in the mt:ATP6[1]/mt:ND2del1+CoIT300I line. The percentage of mt:ATP6[1] in two heteroplasmic lineages (control 1 and control 2) was measured over generations at 29°C. At generation 4, female progeny were divided into two populations: one was mated with males heterozygous for tam3 or tam4 to remove one functional copy of tam and maintained in the heterozygous tam mutant background (balanced by CyO) for the subsequent generations; the other population was mated with KrIf/CyO males as controls. All the controls refer to KrIf/CyO.