Figure 3.
2D Light Pattern Delivery Triggers Focal Activity in Auditory Cortex
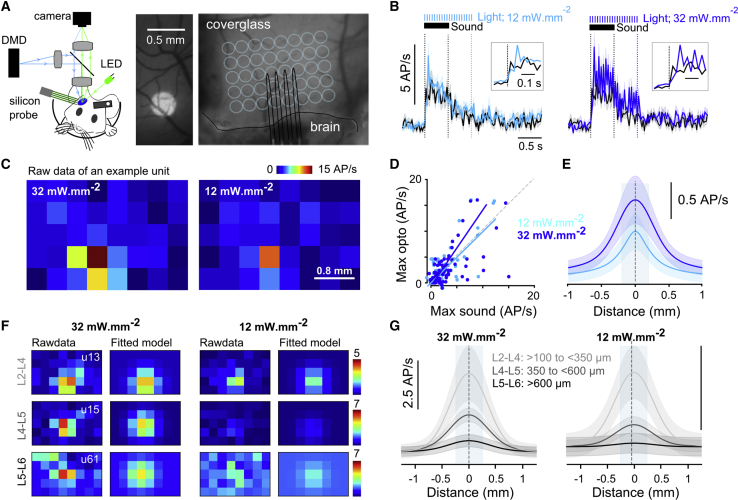
(A) Left: photo-stimulation setup and optogenetic calibration protocol. Center: example image of an ∼400-μm disk projected onto the cranial window is shown. Right: image of the AC cranial window with a sketch of the silicon probe insertion site and grid locations where light was projected is shown (light blue).
(B) Time course of mean firing rate (50-ms time bin) in response to a single pure tone of 500 ms at 70-dB SPL (black line) or in response to 12-mW.mm−2 (left) or 32-mW.mm−2 (right) focal optogenetic stimulations (light blue line; disk diameter 400 μm) for n = 84 single units (shadings represent SEM). Insets: magnification at stimulus onset is shown.
(C) 2D maps of an example single unit for two light intensities, representing the mean firing rate over 10 repetitions during photo-stimulation of the different locations on the grid.
(D) Best photo-stimulation response plotted against best sound response measured as the largest trial-averaged response over a 500-ms window starting at stimulus onset. For 12 mW.mm−2, the slope of the regression line was 1.01 and the correlation coefficient 0.74; p = 2.4 × 10−16; n = 84 single units recorded between 300 and 900 μm in depth.
(E) Mean of Gaussian models that were fitted to the 2D lateral distribution profile of photo-stimulation responses (shadings represent SEM). Half-width diameter: 560 ± 147 μm at 12 mW.mm−2 and 800 ± 235 μm at 32 mW.mm−2 (n = 84 single units).
(F) 2D maps as in (C), together with the fitted 2D Gaussian model for three single units recorded at three different depths (L2–L4: >100 μm to <350 μm; L4 to L5: >350 μm to <600 μm; L5 to L6: >600 μm).
(G) Mean 1D profile of the fitted Gaussian models as in (E) but for each estimated depth range defined in (F) and for each light intensity. Number of cells: 32 mW.mm−2, L2–L4: n = 31, L4 to L5: n = 66, and L5 to L6: n = 47; 12 mW.mm−2, L2–L4: n = 29, L4 to L5: n = 62, and L5 to L6: n = 34.