Figure 2.
Mutations in the WASP CRIB Motif Abrogate Binding to Active Rac1
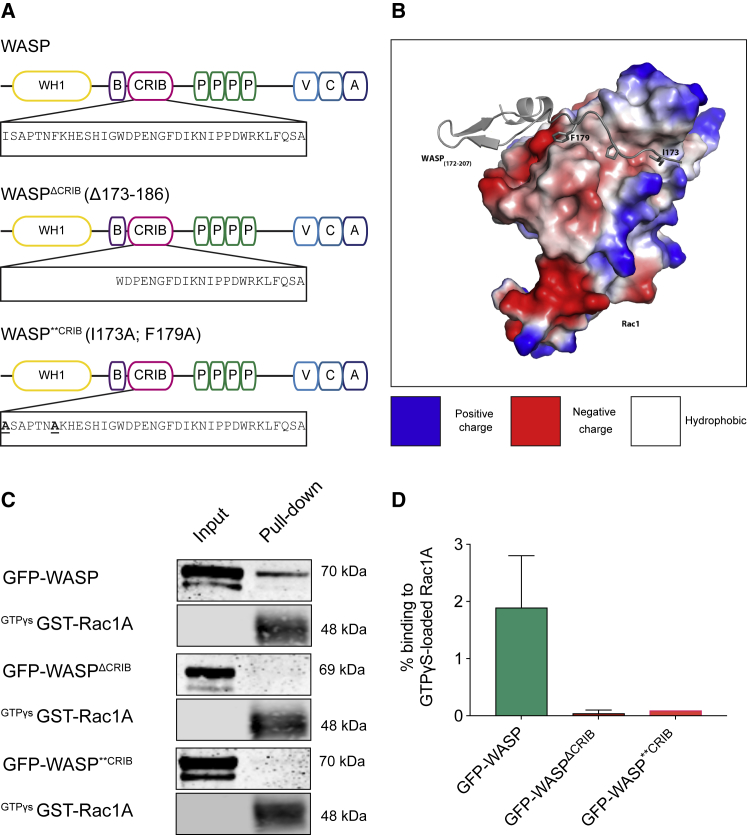
(A) WASP domain composition and mutations introduced within the CRIB motif. From top to bottom: WASP; WASPΔCRIB; and WASP∗∗CRIB are shown.
(B) 3D representation of WASP/Rac1 interface. WASP (gray) residues I173 and F179 establish contacts with a hydrophobic (white) region of Rac1.
(C) GFP-WASP (first panel) interacts with active (GTPγs-bound) Rac1A, GFP-WASPΔCRIB and GFP-ASP∗∗CRIB (third and fifth panels) do not (IB = anti-GFP). Anti-GST immunoblot was performed (second, fourth, and sixth panels) to verify the expression of GST-Rac1A. Related to Figure S2.
(D) Immunoblot quantification shows no binding of GFP-WASPΔCRIB and GFP-WASP∗∗CRIB to active Rac1 (GFP-WASP: 1.9% ± 0.9%; GFP-WASPΔCRIB: 0.05% ± 0.05%; GFP-WASP∗∗CRIB: 0.1; mean ± SEM; n = 3).