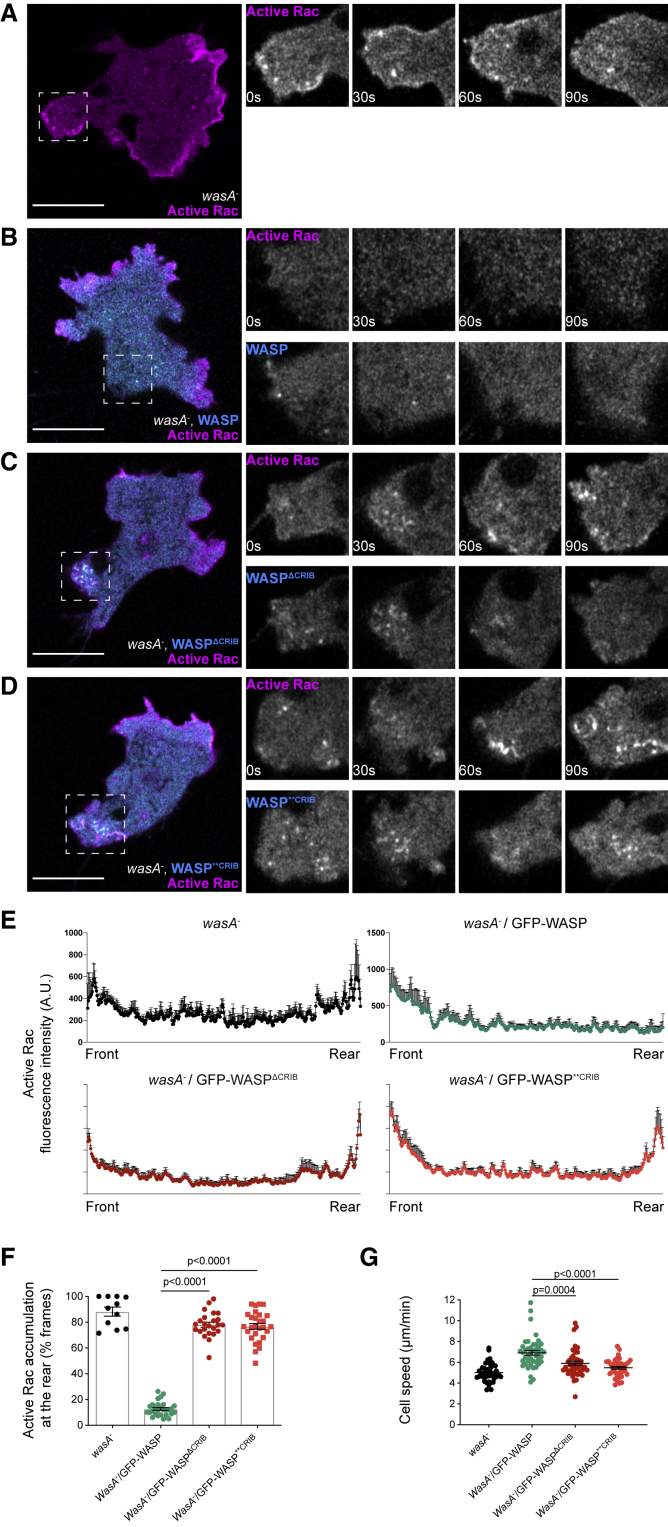
Figure 5.
WASP Requires a Functional CRIB Motif to Confine Active Rac at the Leading Edge during Migration
Live imaging of migrating wasA− cells expressing active Rac marker (PakB CRIB-mRFPmars2). Insets highlight the cells’ rear (squares) at different time points.
(A) Active Rac accumulates at the rear of wasA− cells at all time points. Scale bar represents 10 μm.
(B) In cells expressing GFP-WASP, no sign of active Rac enrichment at the rear can be detected. Scale bar represents 10 μm.
(C and D) In cells expressing GFP-WASPΔCRIB (C) or GFP-WASP∗∗CRIB (D), active Rac can be detected within the enlarged rear. Puncta generated by WASP CRIB mutants cluster at the enlarged rear. Scale bars represent 10 μm. Related to Video S3.
(E) Fluorescence plots reporting the active Rac marker’s intensity at four time points along a line connecting front to rear of wasA− cells (top left), and wasA− cells expressing either WASP (wasA−/GFP-WASP, top right), WASPΔCRIB (wasA−/GFP-WASPΔCRIB, bottom left), or WASP∗∗CRIB (wasA−/GFP-WASP∗∗CRIB, bottom right). Error bars represent SEM.
(F) Frequency of active Rac accumulation at the back of wasA− cells and wasA− cells expressing wild-type WASP or WASP CRIB mutants. wasA− (n = 11 cells): 88.2% ± 3.5%; wasA−/GFP-WASP (n = 28 cells): 12.7% ± 1.0%; wasA−/GFP-WASPΔCRIB (n = 24 cells): 78.1% ± 2.0%; wasA−/GFP-WASP∗∗CRIB (n = 28 cells): 76.7% ± 2.2%; means ± SEM. One-way ANOVA; wasA−/GFP-WASP versus wasA−/GFP-WASPΔCRIB: p < 0.0001; wasA−/GFP-WASP versus wasA−/GFP-WASP∗∗CRIB: p < 0.0001.
(G) Migratory speed of wasA− cells and wasA− cells expressing wild-type WASP or WASP CRIB mutants. wasA− (n = 45 cells): 5.0 ± 0.1 μm/min; wasA−/GFP-WASP (n = 44 cells): 6.9 ± 0.2 μm/min; wasA−/GFP-WASPΔCRIB (n = 44 cells): 5.9 ± 0.2 μm/min; wasA−/GFP-WASP∗∗CRIB (n = 41 cells): 5.5 ± 0.1 μm/min; means ± SEM. Kruskal-Wallis test; wasA−/GFP-WASP versus wasA−/GFP-WASPΔCRIB: p = 0.0004; wasA−/GFP-WASP versus wasA−/GFP-WASP∗∗CRIB: p < 0.0001.