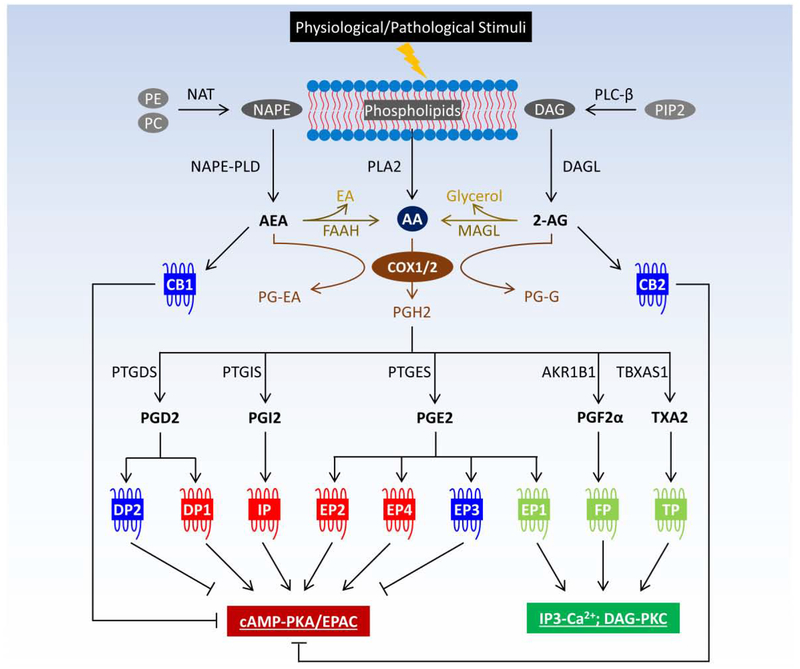
Figure 1.
Crosstalk between prostanoids and endocannabinoids in GPCR signaling. Prostanoids and endocannabinoids are eicosanoids derived from cell membrane-bound phospholipids. Endocannabinoids, such as AEA and 2-AG, can be metabolized to AA, which is the precursor for prostanoid biosynthesis. In addition, COX also metabolizes endocannabinoids to prostaglandin analogs, i.e., PG-EA from AEA and PG-G from 2-AG. Responding to extracellular stimuli, prostanoids and endocannabinoids are rapidly synthesized to mediate wide-ranging physiological and pathological processes via directly acting on a myriad of GPCRs. Abbreviations: 2-AG, 2-arachidonoylglycerol; AA, arachidonic acid; AEA, N-arachidonoylethanolamine; AKR1B1, aldo-keto reductase family 1 member B1 or aldose reductase; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; CB, cannabinoid receptor; COX, cyclooxygenase; DAG, diacyl glycerol; DAGL, diacylglycerol lipase; DP, PGD2 receptor; EA, ethanolamine; EP, PGE2 receptor; EPAC, exchange factor directly activated by cAMP; FAAH, fatty acid amide hydrolase; FP, PGF2α receptor; IP, PGI2 receptor; IP3, inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate; MAGL, monoacylglycerol lipase; NAPE, N-arachidonoyl-phosphatidylethanolamine; NAPE-PLD, N-acylphosphatidylethanolamine-specific phospholipase D; NAT, N-acyltransferase; PC, phosphatidylcholine; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PG, prostaglandin; PG-EA, PG(D2/E2/F2α/I2)-ethanolamide or prostamide; PG-G, PG(D2/E2/F2α/I2)-glycerol ester; PIP2, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; PKA, protein kinase A; PKC, protein kinase C; PLA2, phospholipases A2; PLC-β, phospholipase C-β; PTGDS, PGD2 synthase; PTGES, PGE2 synthase; PTGIS, PGI2 synthase; TP, TXA2 receptor; TBXAS1, TXA2 synthase 1; TX, thromboxane.