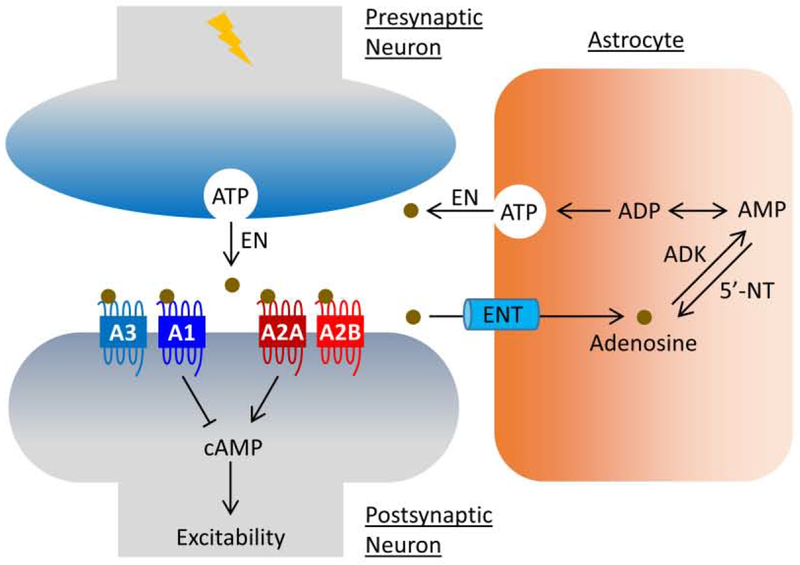
Figure 2.
Adenosine signaling at tripartite synapse. As the primary source of adenosine, ATP is released from astrocytes and neurons via vesicles under normal physiological and pathological conditions, respectively. Upon release, ATP undergoes quick digestion to adenosine by a cascade of EN. Excessive adenosine is then taken up by ENT to astrocytes where it undergoes metabolic clearance by ADK to AMP to complete the balance of the ATP/adenosine conversion cycle. Adenosine regulates neuronal excitability via GPCR-mediated cAMP signaling in the epileptic brain. Abbreviations: 5’-NT, 5′-nucleotidase; A1, adenosine receptor subtype A1; A2A, adenosine receptor subtype A2A; A2B, adenosine receptor subtype A2B; A3, adenosine receptor subtype A3; ADK, adenosine kinase; ADP, adenosine diphosphate; AMP, adenosine monophosphate; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; EN, extracellular ectonucleotidase; ENT, equilibrative nucleoside transporter.