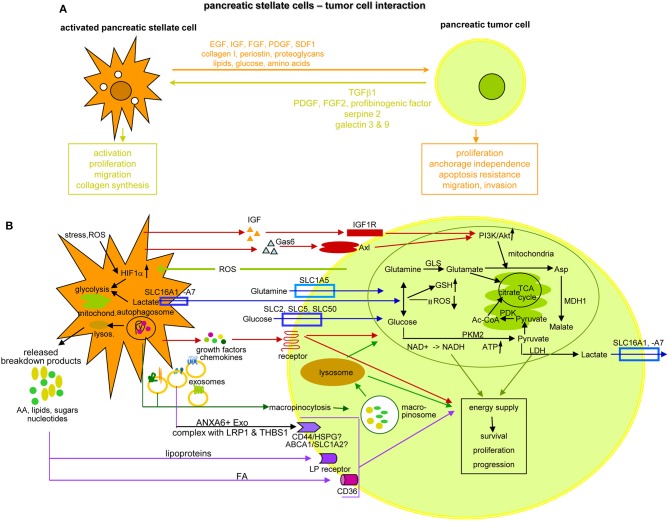
Figure 10.
The crosstalk between PSC and pancreatic cancer cells. (A) Overview of the support provided by aPSC to PaCa survival, expansion and gain in aggressiveness and feedback by the tumor cell, which sustains PSC activation, expansion and matrix protein synthesis. (B) Some of the important components delivered by aPSC toward tumor cells and the initiated changes with a focus on altered metabolism. Glutamate derived from influxed glutamine can replace the TCA cycle to generate citrate, which also can derive from the pyruvate-PDK-Ac-CoA pathway. Lactate, delivered via lactate transporters supports glutamine and glucose generation, GSH upregulation and ROS reduction. Glucose also becomes enriched by glucose transporter in the tumor cell, where PKM2 via NADH and ATP promotes pyruvate generation. After lysosome degradation of aPSC autophagosomes, a plethora of AA, lipids, lipoproteins, sugars, and nucleotides is delivered that in part are taken up by specific receptors, not all being identified so far. Alternatively, autophagosomes are taken up by macropinocytosis, the macropinosome content being delivered after lysosome degradation. Lysosome degradation is also required for the delivery of the aPSC Exo content. Another option is receptor-mediated uptake of selective transmembrane complexes as ANXA61 bound LRP11 and THBS11. The predominant route of transfer from aPSC in PaCa cells is indicated by a color code: red: signaling receptor mediated uptake; blue: delivery or uptake by transporters; vesicle uptake: green; violet: receptor-mediated lipid and lipoprotein uptake; an olive circle encloses for a few of the aPSC-delivered components the pathway, whereby they contribute to the altered metabolism of PaCa cells; others may directly support PaCa survival and aggressiveness. Full name of proteins are listed in Table S1. aPSC support PaCa survival, expansion and progression, which to a considerable degree relies on their input of components initiating energy generation by altered metabolic pathways. Despite the focus on PSC-promoted metabolic adaptation of PaCa cells, the presented data cover only a minor part of the present state of knowledge and additional information can be expected by improved proteomic methodologies combined with organoid cultures.