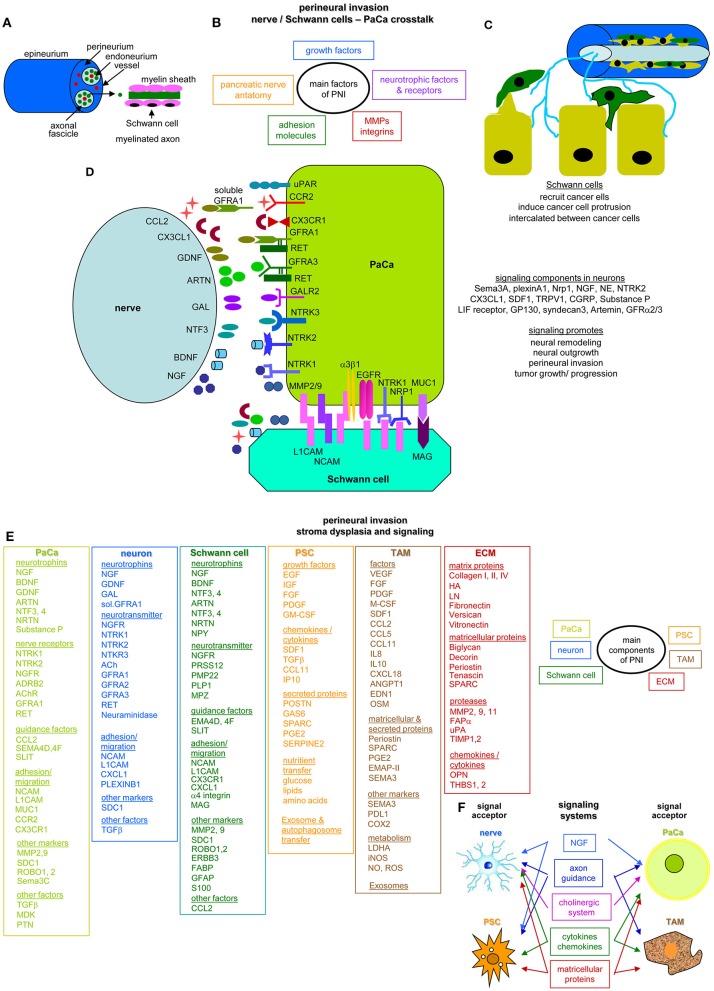
Figure 11.
The nervous system and perineural invasion in pancreatic cancer. (A) Overview of nerve anatomy. The endoneurium surrounds all axons and serves to separate individual nerve fibers. The axons are covered by Schwann cells, where Schwann cells myelinate the axons. Non-myelinating axons mostly ensheath multiple small caliber axons. (B) The anatomy of the pancreatic nerves, neurotrophic factors and receptors as well as growth factors expressed by the engaged cells all contribute to perineural invasion and are supported by adhesion molecules and proteases as demonstrated in (C) for Schwann cells that intercalate between tumor cells promoting destruction of the adhesive matrix and actively recruiting tumor cells toward the nerve by signaling via adhesion molecules that promote cytoskeleton reorganization associated with acquisition of a motile phenotype. (D) Overview of abundantly delivered neurotrophic factors, cytokines, and chemokines by neurons and the corresponding receptors on PaCa tumor cells that promote tumor cell growth and invasion; dominating in the interaction between Schwann cells and tumor cells are L1CAM and NCAM. Besides homophilic binding, they bind integrins and RTK. MAG binding MUC1 on tumor cells mainly contributes to adhesion. For detailed information on signaling cascade initiation in PaCa, please see reviews mentioned in the text file. (E) Besides the direct engagement of neurons, Schwann cells and tumor cells, PSC, TAM, and the dysplastic tumor matrix contribute to PNI. Molecules predominantly contributing to PNI are listed. Selective contributions of aPSC rely predominantly on the transfer of nutrients, Exo and autophagosomes; TAM contribute by the delivery of matricellular proteins like EMAP-II and metabolism regulators such as LDHA and iNOS, the ECM supports PNI by embedded matricellular proteins and proteases. (F) All engaged cell populations are also acceptors of signaling cascade activators such as NGF, axon guidance cytokines/chemokines, and matricellular proteins. Activation of the cholinergic system is of major relevance for nerves and tumor cells. Full name of proteins are listed in Table S1. PNI is one of the dominating pathways of PaCa invasion. It is supported by neurotrophins and neurotransmitters delivered by neurons and Schwann cells, the latter in addition providing guidance factors and membrane integrated proteins that promote adhesion and migration. aPSC are essential in nutrient transfer and TAM provide cue enzymes to cope with ROS and NO. TAM and the ECM contribute by matricellular proteins and proteases that facilitate PaCa cell migration toward the nerve.