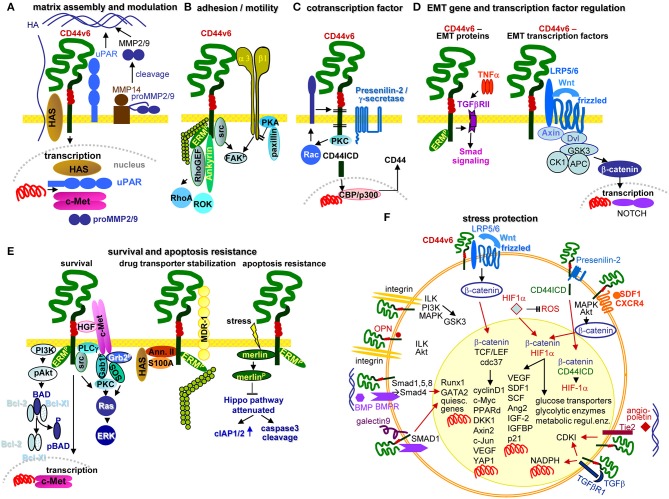
Figure 5.
Multifaceted activities of CD44v6 in PaCIC. (A) Upon HA crosslinking, CD44v6 initiates HAS, uPAR, MMP2, and MMP9 transcriptions, which promote HA assembly and matrix remodeling, where MMP14 contributes to proMMP2 and MMP9 cleavages. (B) CD44v6 can associate with α3β1 such that both molecules jointly contribute to FAK activation and motility. (C) CD44v6 can be cleaved by TACE and subsequently by the presenilin2 complex. The CD44ICD acts as a cotranscription factor, which together with CBP/p300 promotes CD44 transcription (D) By TNFα associating with TGFβRII, EMT protein expression is supported via Smad signaling. The association of CD44v6 with LRP5/6 supports Wnt/frizzled activation such that β-catenin leaves the suppressive complex and acts as cotranscription factor in NOTCH transcription. (E) There are several pathways whereby CD44v6 strengthens PaCIC survival and apoptosis resistance. cMET comes into proximity of CD44v6 via CD44v6-bound HGF. This initiates activation of the PI3K/Akt anti-apoptotic and of the Ras-ERK pathways. In addition, CD44v6 supports cMET transcription. A complex of CD44v6 with HAS, Annexin II, S100A, and activated ERM stabilizes MDR1 expression, which contributes to drug efflux. Finally, stress induces the association with and dephosphorylation of merlin, which attenuates the HIPPO pathway with upregulation of cIAP1/2 and caspace3 cleavage. (F) Some of the multiple activities of CD44v6 in stress protection via affecting the cells metabolism are summarized indicating whether altered metabolism is promoted by signaling cascades in the cytosol or depends on transcriptional activation (red arrows). The latter accounts particularly for β-catenin-TCF/LEF, β-catenin-HIF1α, and β-catenin-CD44ICD complexes, but also for the cooperation of CD44v6 with Tie2, TGFβR1, galectin 9, and BMPR, which affect transcription of a large range of distinct genes. Full name of proteins are listed in Table S1. CD44v6 is engaged in most steps of the metastatic cascade. The strongest impacts are seen in terms of survival, EMT induction and metabolic changes that guarantee unimpaired survival under hypoxic and poor nutrient conditions.