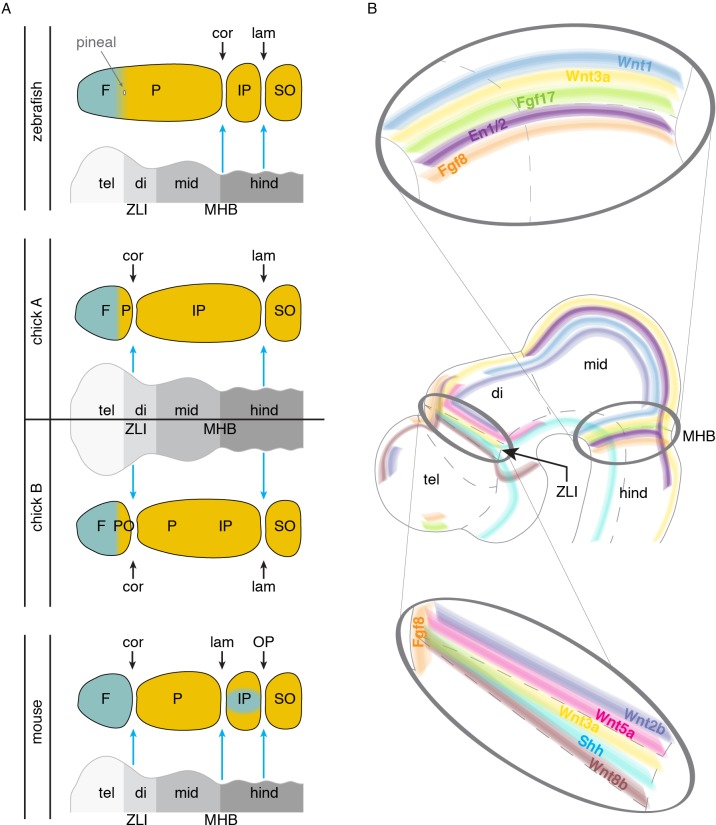
Figure 4. Models of brain to skull interactions across vertebrates.
(A) Cranial bones are depicted relative to embryonic brain, with crest-derived bone in teal and mesoderm-derived bone in yellow. Comparison of zebrafish, chick, and mouse proposes the zona limitans intrathalamica (ZLI) and midbrain-hindbrain boundary (MHB, or isthmic organizer) as major signaling centers for suture development. For chick, two interpretations are shown: ‘chick A’ in which the mesoderm-derived portion of the ‘frontal’ bone is homologous to the anterior part of the mammalian parietal, and ‘chick B’ in which the mesoderm-derived postorbital is fused to the frontal. (B) Signaling molecules enriched at the ZLI and MHB include Wnts, Fgfs, En1/2, and Shh, all of which have known roles in proper skull and suture formation. F, frontal; P, parietal; IP, interparietal; SO, supraoccipital; PO, postorbital; tel, telencephalon; di, diencephalon; mid, midbrain; hind, hindbrain; ZLI, zona limitans intrathalamica; MHB, midbrain-hindbrain boundary; cor, coronal suture; lam, lambdoid suture; OP, occipitointerparietal suture.