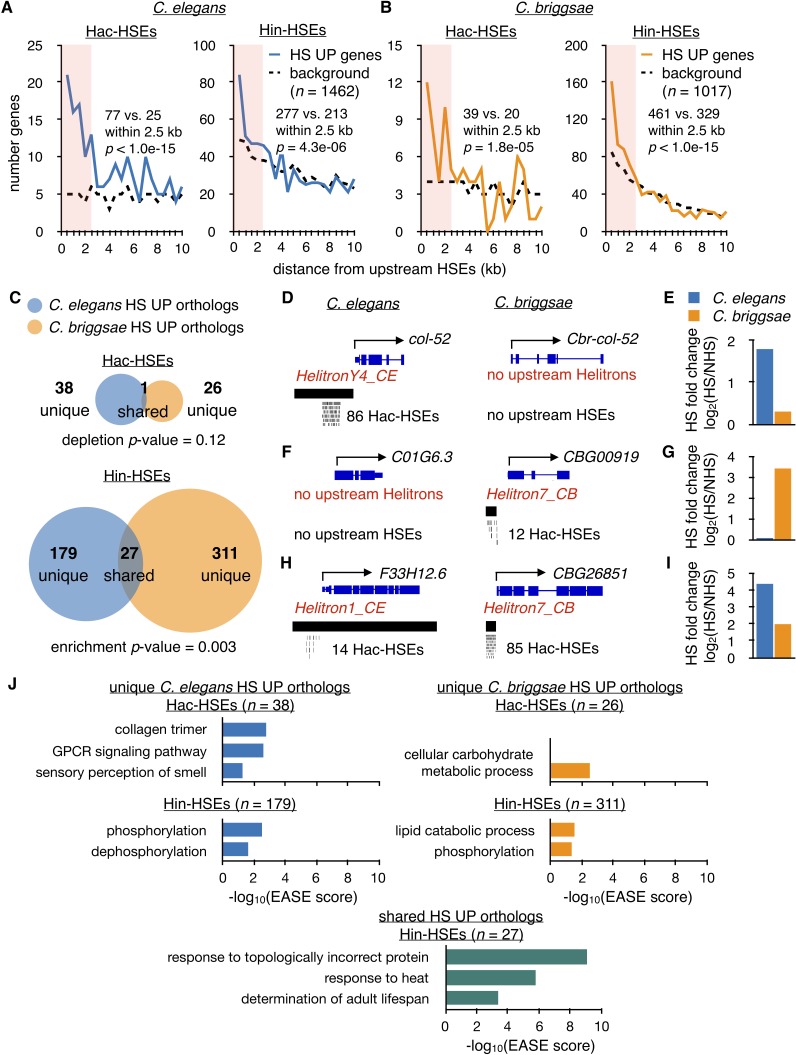
Figure 4. Hac-HSEs are associated with distinct gene sets up-regulated by HS in C. elegans and C. briggsae.
(A) Number of C. elegans HS UP genes (n = 1462) within 500 bp bins vs. distance from Hac- and Hin-HSEs. HS UP genes are defined as those with a fold change after HS >2 and an adjusted p-value<0.01 determined using DESeq2 (Love et al., 2014). Solid blue lines represent numbers of HS UP genes observed, while black dashed lines represent background numbers resulting from chance. Seventy-seven HS UP vs. 25 expected genes have Hac-HSEs within 2.5 kb upstream, resulting in significant enrichment (p<1.0e-15, χ2 test). Two hundred and seventy-seven HS UP vs. 213 expected genes have Hin-HSEs within 2.5 kb upstream, resulting in significant enrichment (p=4.3 e-06, χ2 test) (B) Number of C. briggsae HS UP genes (n = 1017) within 500 bp bins vs. distance from Hac- and Hin-HSEs. Solid orange lines represent numbers of HS UP genes observed, while dashed black lines represent background numbers resulting from chance. Thirty-nine HS UP vs. 20 background genes have Hac-HSEs within 2.5 kb upstream, resulting in significant enrichment (p=1.8e-05, χ2 test). Four hundred and sixty-one HS UP vs. 329 background genes have Hin-HSEs within 2.5 kb upstream, resulting in significant enrichment (p<1.0e-15, χ2 test). (C) Venn diagrams showing overlap of orthologous HS UP genes in C. elegans (blue) and C. briggsae (orange) that have Hac- or Hin-HSEs within 2.5 kb upstream in both species. Unique HS UP orthologs have upstream HSEs in either C. elegans or C. briggsae, while shared HS UP orthologs have upstream HSEs in both species. There is significant enrichment in the overlap of C. elegans Hin-HSE genes with C. briggsae orthologs up-regulated after HS (p=0.003, hypergeometric test). (D) Genome browser screenshots of C. elegans col-52 and its C. briggsae ortholog Cbr-col-52. C. elegans col-52 has 86 upstream Hac-HSEs supplied by a copy of HelitronY4_CE and Cbr-col-52 lacks upstream Hac-HSEs. (E) HS fold-change values for C. elegans col-52 (blue) (3.5 fold) and C. briggsae Cbr-col-52 (orange) (1.2 fold) determined using DESeq2. (F) Genome browser screenshots of C. elegans C01G6.3 and its C. briggsae ortholog CBG00919. C01G6.3 lacks upstream Hac-HSEs and CBG00919 has 12 Hac-HSEs provided by a copy of Helitron7_CB. (G) HS fold-change values for C. elegans C01G6.3 (blue) (1.1 fold) and C. briggsae CBG00919 (orange) (11 fold) determined using DESeq2. (H) Genome browser screenshots of C. elegans F33H12.6 and its C. briggsae ortholog CBG26851. F33H12.6 resides within a full-length copy of Helitron1_CE and has 14 upstream Hac-HSEs. CBG26851 has 85 upstream Hac-HSEs supplied by a copy of Helitron7_CB. (I) HS fold-change values for C. elegans F33H12.6 (blue) (21 fold) and C. briggsae CBG26851 (orange) (4.0 fold) determined using DESeq2. (J) Significantly-enriched gene ontology (GO) terms identified using DAVID (Huang et al., 2009a; Huang et al., 2009b) for unique Hac- and Hin-HSE up-regulated orthologs in C. elegans (blue) and C. briggsae (orange), as well as shared Hin-HSE up-regulated orthologs (aquamarine).