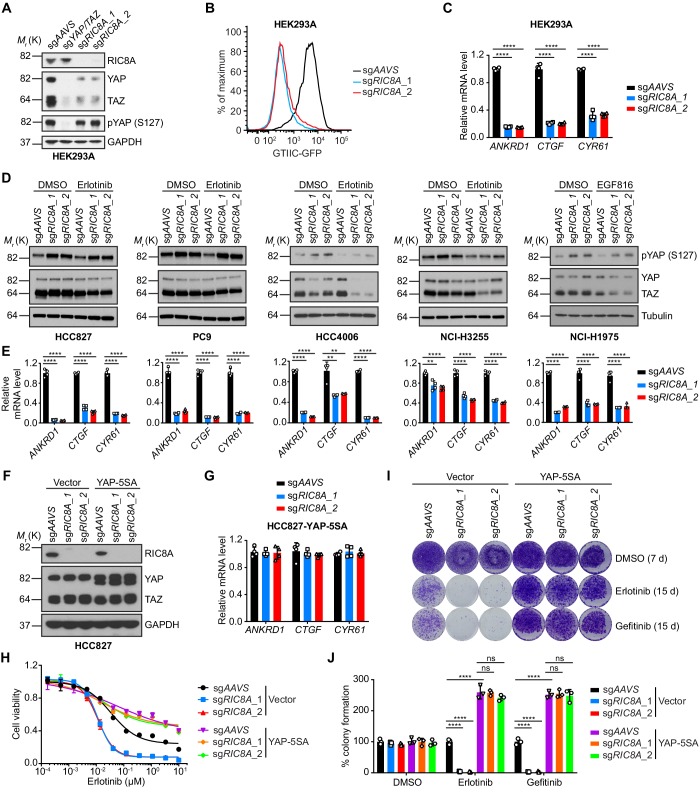
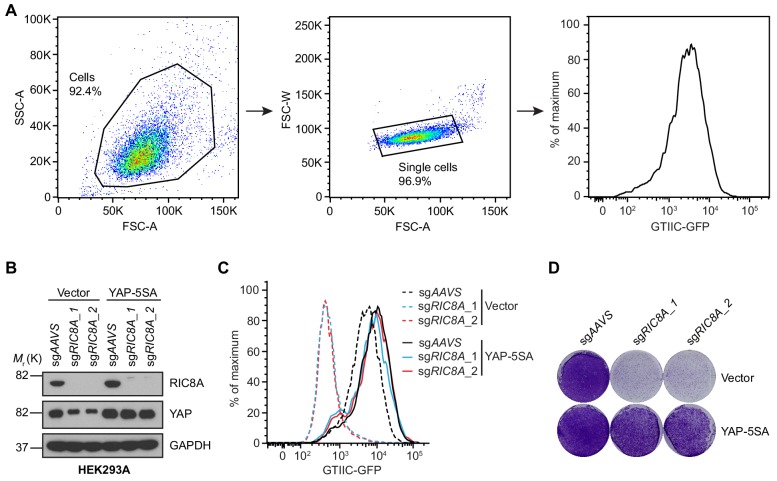
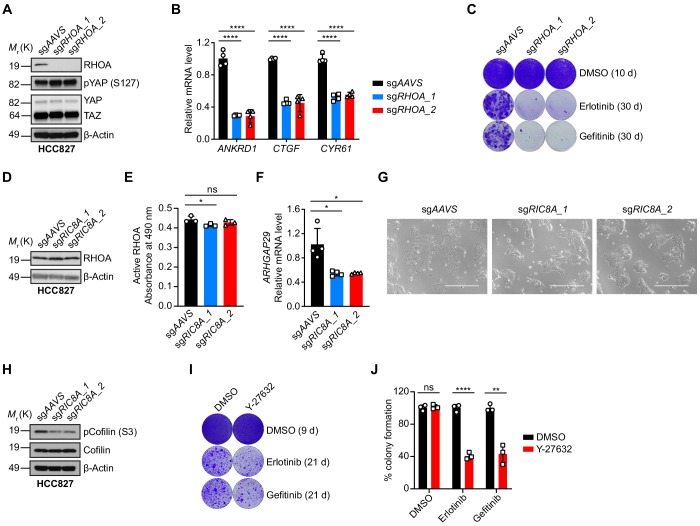
Figure 4. RIC8A loss attenuates YAP signaling to synergize with EGFR-TKI in EGFR-mutant NSCLC.
(A) Immunoblots of indicated proteins in HEK293A cells upon knockout of indicated genes. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (B) RIC8A knockout decreases the YAP reporter activity in HEK293A cells, assessed by flow cytometry analysis of GFP. (C) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of relative mRNA levels of YAP target genes in control or RIC8A knockout HEK293A cells. Error bars represent mean ± SD; n = 4. (D) Immunoblots of pYAP (S127) and YAP/TAZ in indicated EGFR-mutant NSCLC cell lines treated with DMSO or 1 µM EGFR-TKI (Erlotinib, except EGF816 for NCI-H1975) for 24 hr. Tubulin was used as a loading control. (E) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of relative mRNA levels of YAP target genes in control or RIC8A knockout EGFR-mutant NSCLC cell lines. Error bars represent mean ± SD; n = 4. (F) Immunoblots of RIC8A and YAP/TAZ in indicated HCC827 cells to confirm RIC8A knockout and YAP-5SA overexpression. GAPDH was used as loading control. (G) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of relative mRNA levels of YAP target genes in control or RIC8A knockout HCC827 cells with ectopic expression of constitutively active YAP (YAP-5SA). Error bars represent mean ± SD; n = 4. (H) Cell viability assessment by CellTiter-Glo assay of indicated HCC827 cell lines treated with serial dilutions of erlotinib for 72 hr. Error bars represent mean ± SD; n = 4. (I) Crystal violet staining colony formation assay of indicated HCC827 cell lines treated with DMSO, erlotinib (1 µM), or gefitinib (1 µM). (J) Quantification of colony formation in (I), shown as percentage of the Vector-sgAAVS sample. Error bars represent mean ± SD; n = 3. Statistical significance was tested using unpaired two-tailed t test (C and E) or ordinary two-way ANOVA (J); *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001; ns, not significant.