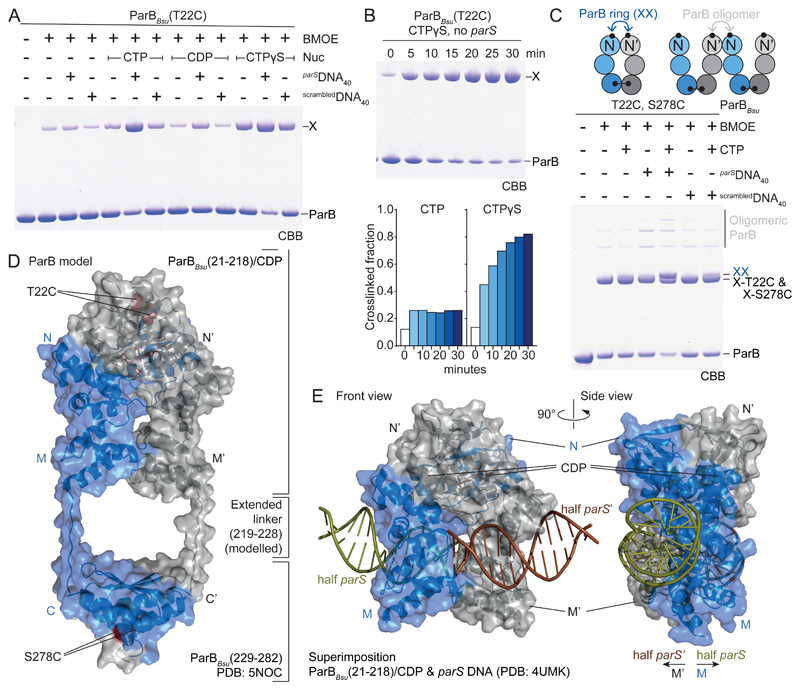
Fig. 3. ParB gate closure.
(A) Gel analysis of cross-linking products of purified ParBBsu(T22C). X denotes cross-linked species. CBB, Coomassie Brilliant Blue. (B) Time-course of ParBBsu(T22C) cross-linking with CTPγS without parS. Aliquots were taken at the indicated time points and mixed with BMOE. Quantification of cross-linked fraction also shown for CTP (see fig. S6B). (C) As in A using ParBBsu(T22C, S278C). X-T22C and X-S278C denote single cross-linked dimer species. XX marks double cross-linked ParB rings. Other species are oligomeric forms. (D) Model of ParB built from ParBBsu(21-218)/CDP/Ca2+ and ParBBsu(229-282) (PDB: 5NOC) dimers. Linker at the M-C junction is manually modelled as fully extended peptide. (E) Superimposition of domain M in ParBBsu(21-218)/CDP/Ca2+ and a ParB/parS structure (PDB: 4UMK). Only DNA is shown for the latter.