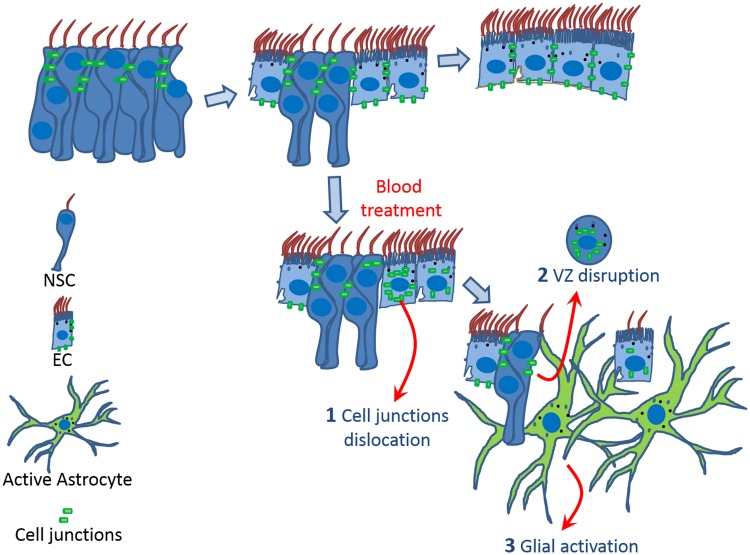
FIGURE 5.
Model summarizing the effects of the blood on the VZ. During maturation (A–C), neural stem cells (NSC) with adherens junctions transform into multiciliated ependymal cells (EC). Blood exposure produces a time-dependent chain of events starting with the dislocation of cell junctions (N-cadherin) from the cell membrane into the cytoplasm and loss of multiciliated cells. Subsequently, glial activation occurs, as evidenced by astrocytes with numerous processes. In vivo observations suggest that glial activation occurs at the site of VZ disruption.