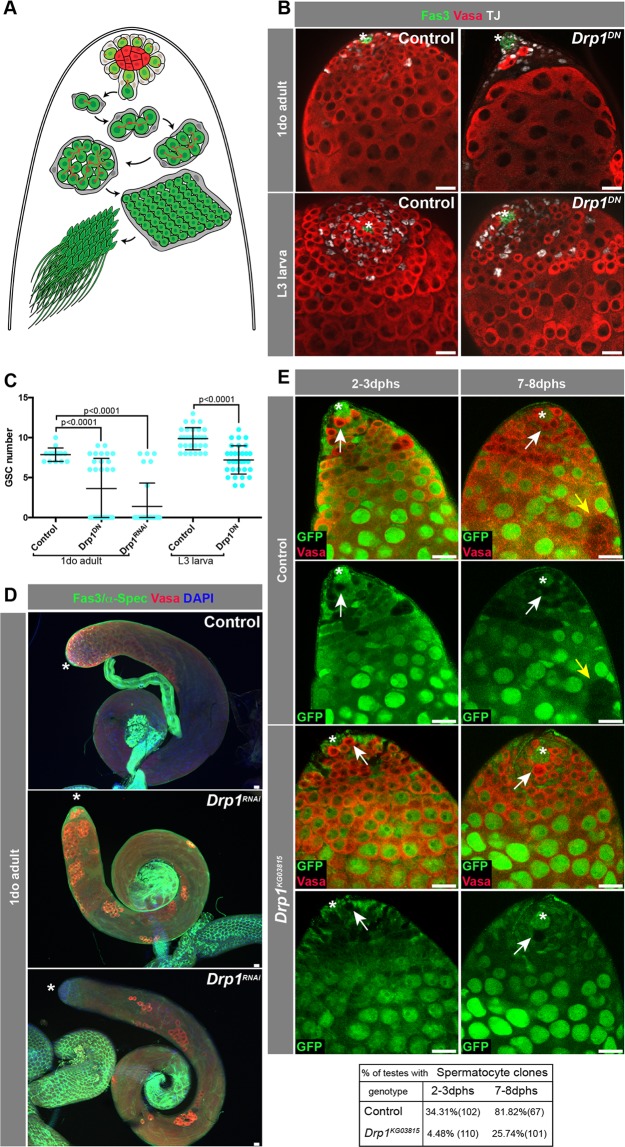
Figure 1.
Drp1 is required for GSC maintenance in larval stages. (A) Schematic of the Drosophila testis. Hub cells (red) are surrounded by two stem cell populations: GSCs (in green) and CySCs (in gray). CySCs give rise to CCs that accompany the developing germline until spermiogenesis. GSCs divide to self-renew and give rise to a gonialblast, which undergoes four rounds of TA divisions prior to undergoing meiosis and terminal differentiation into sperm. (B) Representative immunofluorescence images of testes from ‘control’ (nanosGAL4:VP16 > w1118) and ‘Drp1DN’ (nanosGAL4:VP16 > Drp1DN) flies at 1 day old (do, post eclosion) or L3 larval stage. (C) Quantification of GSC number. Two-tailed t-test used. (D) Examples of testes from 1do animals. Note the range of distribution in the nanosGAL4:VP16 > Drp1RNAi animals (with and without GSCs). (E) Representative images of FRT-mediated clonal generation in control and Drp1KG03815 backgrounds. Clones are marked by the absence of GFP (see Methods). GSC clones are pointed by white arrows, while spermatocyte clones are pointed by yellow arrows. Quantification of clones at different time points (dphs, days post heat shock) displayed in adjacent table. GSC clones were quantified in19. In all images, asterisk (*) represents the hub; Scale bars, 20 μm. Individual images representative of >20 samples acquired from 3 biological replicates.