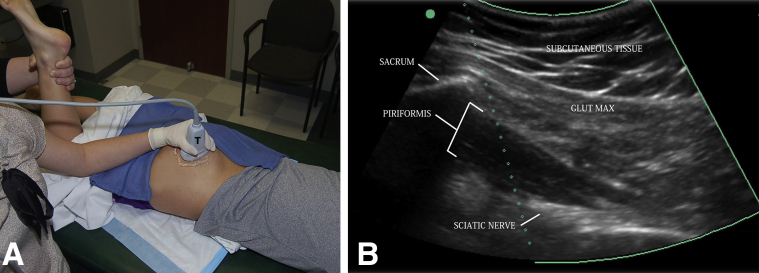
Fig 2.
(A) Inspection of the right piriformis is performed with the patient prone and the transducer (T) placed firmly over the piriformis in the long axis. With the knee flexed, an assistant can internally and externally rotate the leg, allowing visualization of the piriformis in motion throughout the subgluteal space. (B) A long-axis ultrasound image depicts the relation between the subcutaneous tissue, sacrum, gluteus maximus (Glut Max), piriformis, and sciatic nerve.
(All rights are retained by Dr. Byrd.)