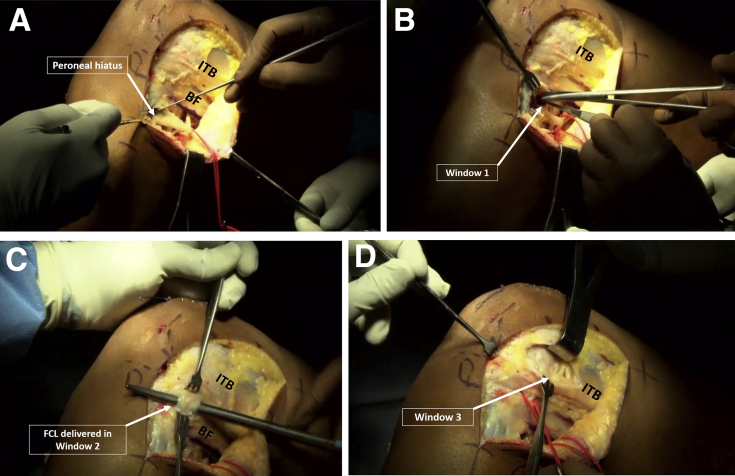
Fig 5.
Common peroneal nerve neurolysis and creation of soft-tissue windows. A left knee is viewed from the left side. (A) The first step in dissection of the lateral side of the knee is to perform a careful common peroneal nerve neurolysis extending from the peroneal hiatus in the peroneus longus muscle distally, up to a distance of 6 cm proximally. (B) Window 1 is created through the peroneal fascia posterior to the fibula styloid and extending medially to access the posterior tibial popliteus sulcus, about 1 cm distal to the joint line. (C) Window 2 is created between the biceps femoris tendon (BF) and iliotibial band, and the fibular collateral ligament (FCL) is visualized here. (D) Window 3 is created by longitudinally incising the iliotibial band (ITB) to access the lateral aspect of the femoral condyle. The lateral epicondyle and popliteus sulcus need to be identified here.