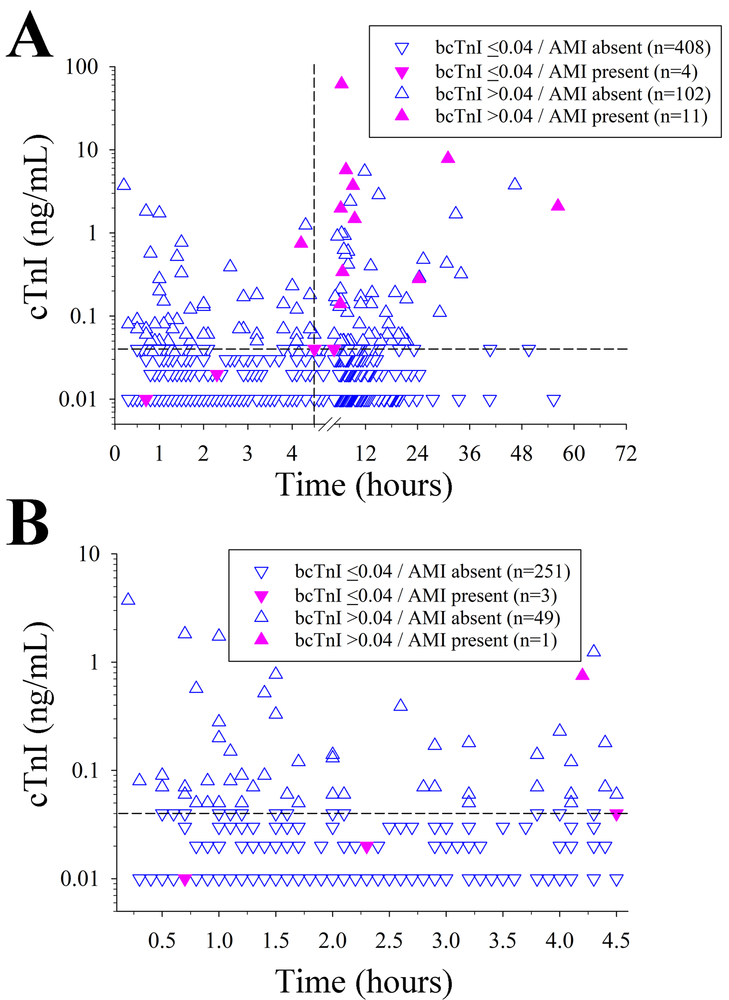
Figure 1.
(A) Relationship between time to baseline cardiac troponin I (bcTnI) and diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction (AMI) in all included patients indicates that significantly fewer patients (p=0.013) were diagnosed with AMI within the first 4.5 hours from symptom onset (n=4 [1.3%]) than afterwards (n=11 [5.0%]). (B) When focusing on the subset of patients with bcTnI assessment within 4.5 hours of symptom onset, only a single patient diagnosed with AMI had an elevated bcTnI (assessed at 4.2 hours, bcTnI = 0.75 ng/mL). Vertical dashed line indicates the 4.5 hour time point. Horizontal dashed line indicates the 0.04 ng/mL cTnI cut off.