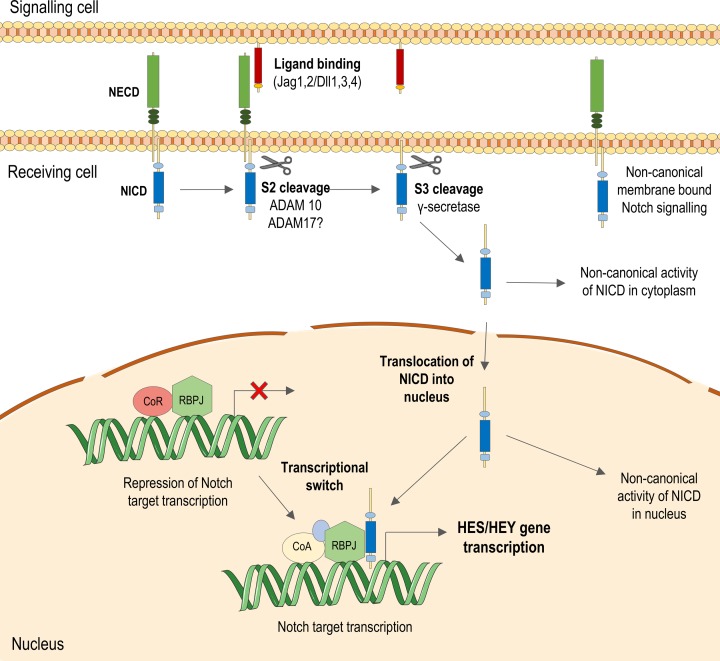
Figure 1. The canonical Notch signalling pathway.
In the canonical Notch pathway, a ligand physically interacts with and binds to the NECD on an adjacent cell. This induces cleavage events by two sheddases, ADAM10 and γ-secretase, allowing cleaved NICD to translocate to the nucleus. In the nucleus, the NICD binds to recombining binding protein suppressor of hairless (RBP-Jκ) and recruits co-activators including Mastermind-like (MAML), which stabilises the interaction between the NICD and RBP-Jκ. This complex promotes transcription of Notch target HES and HEY genes. These transcription factors then affect expression of many more genes involved in processes such as cell cycle progression, survival, and cellular phenotype. Non-canonical Notch signalling pathways are also indicated.