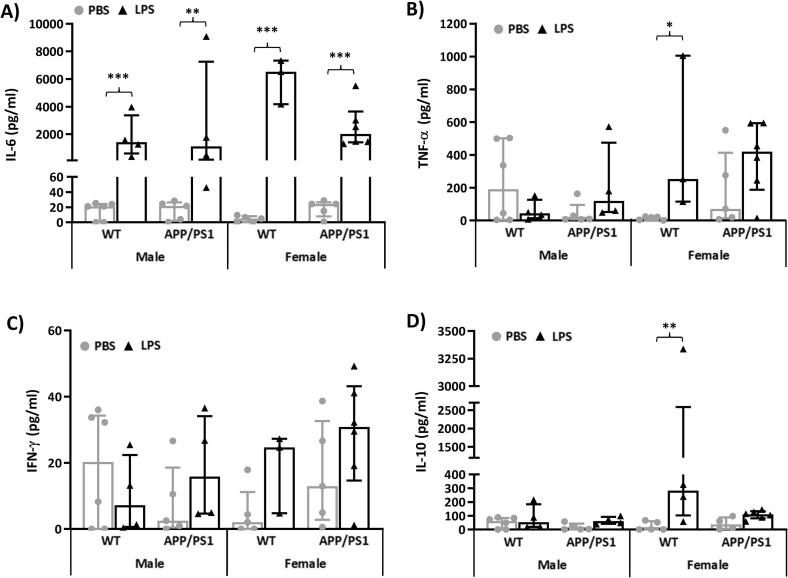
Fig. 2.
LPS-induced plasma cytokines at 4 h post-injection. 4.5-month-old male and female APP/PS1 mice and their wild-type (WT) littermates were challenged with LPS (100µ/kg i.v.) or its vehicle PBS. Their plasma was collected 4 h later, immediately after behavioural assessment, for measurement of induced levels of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines. At this time point, a significant increase in circulating Interleukin 6 (IL-6, A), which has both pro- and anti-inflammatory effects, was observed regardless of sex and genotype (A). Levels of the pro-inflammatory cytokine tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) were increased by LPS in females, particularly WT females (B), but the levels of the other pro-inflammatory mediator, interferon gamma (IFN-γ), were unaltered (C). A significant increase in circulating levels of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10, was also observed in females, regardless of genotype (E). Data were rank-transformed for statistical analyses but are expressed as Median ± interquartile range of non-normalised responses. Dots represent individual animals. Pairwise comparisons: *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.0001 vs PBS.