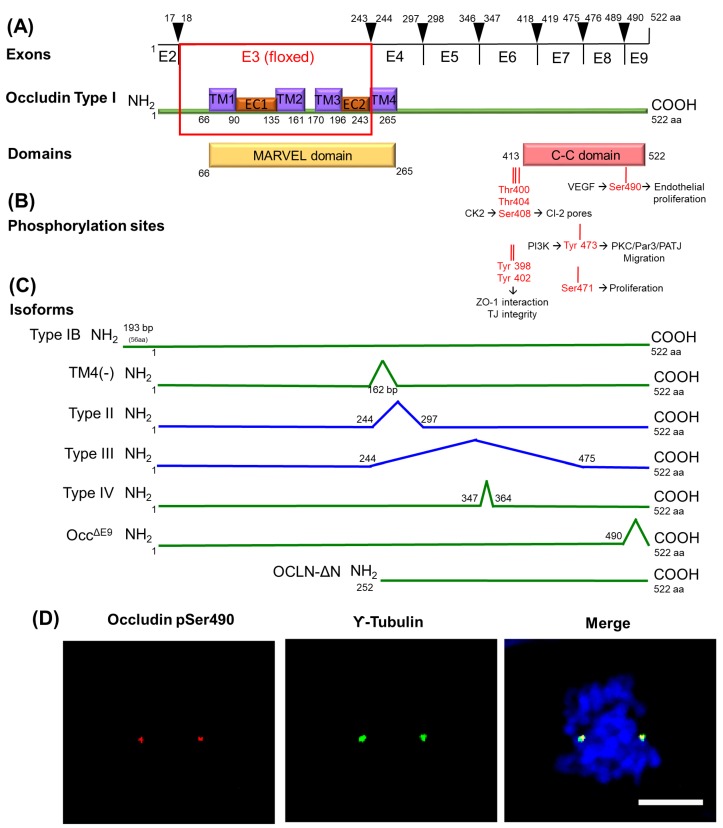
Figure 5.
Occludin structure and isoforms. Occludin is a 522 amino acids protein encoded by 9 exons (A). Occludin full length (type I) possesses four transmembrane (TM) domains and two extracellular (EC) loops with the MARVEL domain as homology on the cytoplasmic side after each TM region. At the C-terminus (COOH) of occludin, a coiled-coiled (C-C) domain can be phosphorylated at multiple sites (B). Phosphorylation of occludin identified and known or implied functions. Occludin can mediate proliferation though the phosphorylation of two sites: Ser471, which regulates post contact proliferation in epithelial cells, and Ser490, which is promoted by VEGF-induced PKCβ activation and regulates both endothelial permeability and neovascularization. To date, several occludin isoforms have been described (C). The function of each isoform has not been fully elucidated, but most isoforms localize to the junctions except type II and III (blue lines). Interestingly, occludin deleted in exon 9 (Occ∆E9) restricts cell migration. (D) In bovine retinal endothelial cells, occludin stained with a pS490-specific antibody (red) shows co-localization of phospho-occludin with the centrosome marker γ-tubulin (green) in pro-metaphase. Hoechst dye (blue). Scale bar = 5 µm.