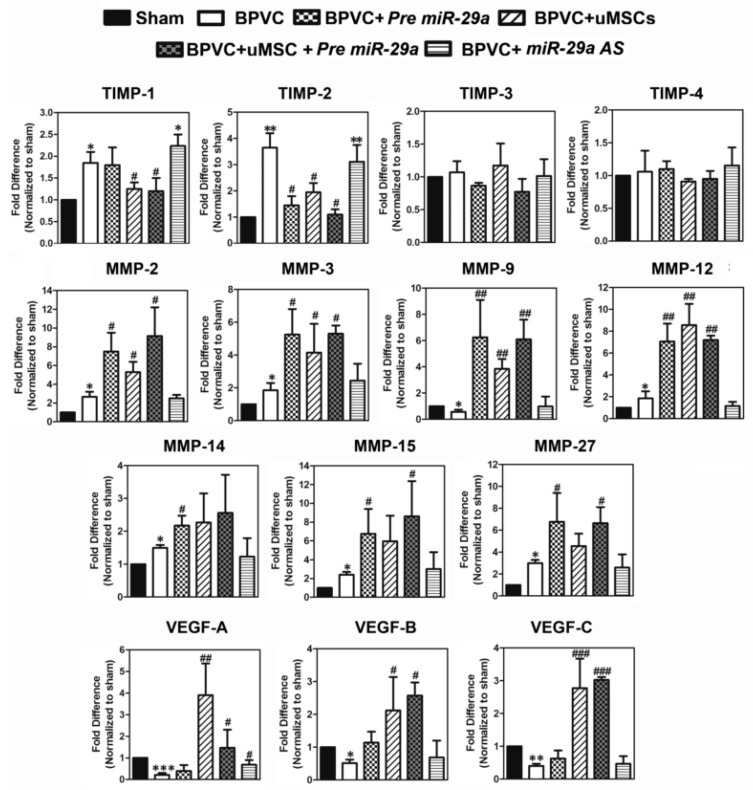
Figure 4.
Effects of exogenously introduction of miR-29a or transplantation of uMSCs on the expression of mouse tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs), matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), and vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGF) in isolated gastrocnemius muscles underwent BPVC-induced ischemic injury. Tissue extracts were collected from gastrocnemius muscles on day 7 post saline or BPVC injection, or after four days of Pre miR-29a, miR-29a AS, and uMSC transplantation 72 h following BPVC-injection. The protein levels of anti-angiogenic factors TIMPs and known pro-angiogenic factors MMPs and VEGFs, responsible for cleaving various extracellular proteins to enhance the tube formation and promote vascular development, with each group of mice were determined using the Quantibody Mouse Angiogenesis Array (n = 6/group). Data were given as means ± SD; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 for the BPVC group vs. the Sham group; # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, ### p < 0.001 for the BPVC group vs. the Sham group; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 for the BPVC + Pre miR-29a group, the BPVC + miR-29a AS group, the BPVC + uMSC group, the BPVC + uMSC + Pre miR-29a group vs. the BPVC group.