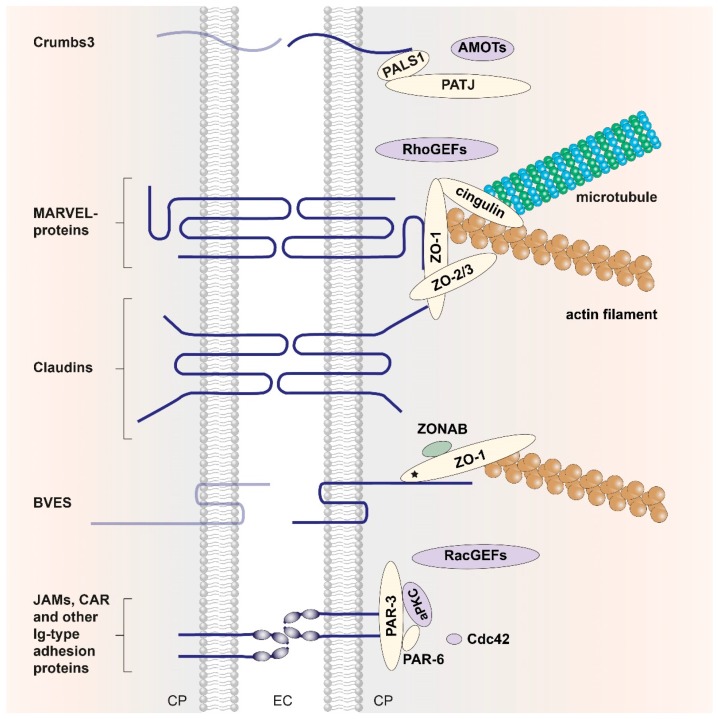
Figure 1.
The tight-junction core structure. TM proteins of the TJ (dark blue) interact with a complex cytoplasmic protein network, the cytoplasmic plaque (shown on the right), providing a physical link to the cytoskeleton (microtubules, actin filaments). Cross-membrane interactions between TM proteins are indicated schematically. For some TM proteins (shown in pale blue) there is no direct evidence for a trans pairing interaction between TM proteins of opposing cells. The cytoplasmic plaque is composed of scaffolding proteins (yellow ovals) that associate with signaling proteins (purple ovals) and (post)transcriptional regulators (green oval), forming the zonular signalosome [23]. The three major protein complexes located in the cytoplasmic plaque are depicted. Within the ZO complex, ZO proteins are present as homodimers or ZO-1/ZO-2 and ZO-1/ZO-3 heterodimers [24] that directly associate with integral TJ membrane proteins through multiple interactions. The polarity complexes PAR-3/PAR-6/aPKC and Crumbs/PALS1/PATJ are responsible for the development of the apico-basal axis of epithelial cells and act as apical components of TJs. TM proteins: Crumbs homolog 3 (CRB3); MARVEL-domain containing proteins occludin, tricellulin, and MARVEL domain-containing protein 3 (MARVELD3); the claudins; the protein blood vessel epicardial substance (BVES); immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily members such as junctional adhesion molecules (JAMs) and the coxsackievirus–adenovirus receptor (CAR). Cytoplasmic scaffolding proteins: Zonula occludens (ZO) proteins ZO-1, ZO-2, and ZO-3; partitioning defective 3/6 homologs (PAR-3, PAR-6); protein associated with Lin-7 1 (PALS1); PALS1-associated tight junction (PATJ) protein; cytoskeletal linker cingulin. Signaling proteins: Atypical protein kinase C (aPKC); proteins of the angiomotin family (AMOTs) [25]; the small Rho-GTPase Cdc42, and guanine nucleotide exchange factors for the Rho-GTPases RhoA (RhoGEFs, e.g., ARHGEF11 [26]) and Rac1 (RacGEFs, e.g., Tiam-1 [27]), respectively. Transcriptional regulator: ZO-1–associated nucleic acid-binding protein (ZONAB, YBX3 in human) [28]. Figure modified and updated after Zihni et al. [12].