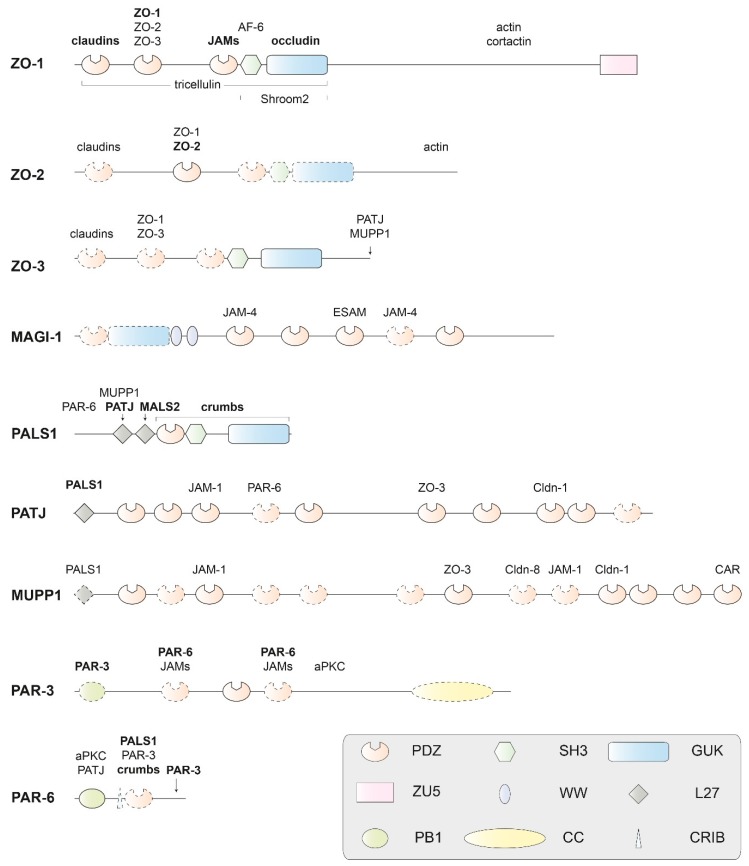
Figure 6.
Domain structure of human PDZ domain-containing adapter proteins of the cytoplasmic plaque that interact physically with TM proteins of the tight junction. The proteins are scaled to the length of their amino-acid sequences. Experimental structures (usually by X-ray or NMR analysis) are available for protein domains drawn with solid contours, but not for domains drawn with dashed contours or for extended regions of polypeptide chains without domain annotation. Proteins binding to components of the human cytoplasmic plaque or their homologs are indicated above or below their interacting domains. With the exception of aPKC (as a subunit of the PAR-3/PAR-6/aPKC complex), only TM proteins or classical adapter proteins of the TJ are included as interacting proteins. Names of interacting proteins are written in bold letters, where the interaction is structurally characterized. Protein names and abbreviations are explained in the text or the legend of Figure 1. Domains are abbreviated as follows: PDZ: Initially identified in PSD-95 (postsynaptic density-95); DLG-1 (the Drosophila tumor suppressor protein discs large 1) and ZO-1; SH3: Src homology-3; PB1: Initially identified in PHOX and BEM1; ZU5: Present in ZO-1 and UNC5; L27: LIN-2/LIN-7; GUK: guanylate kinase homolog; WW: Named after two signature tryptophan residues; CC: coiled-coil; CRIB: CDC42/RAC interactive binding. Figure modified and updated after Guillemot et al. [3].