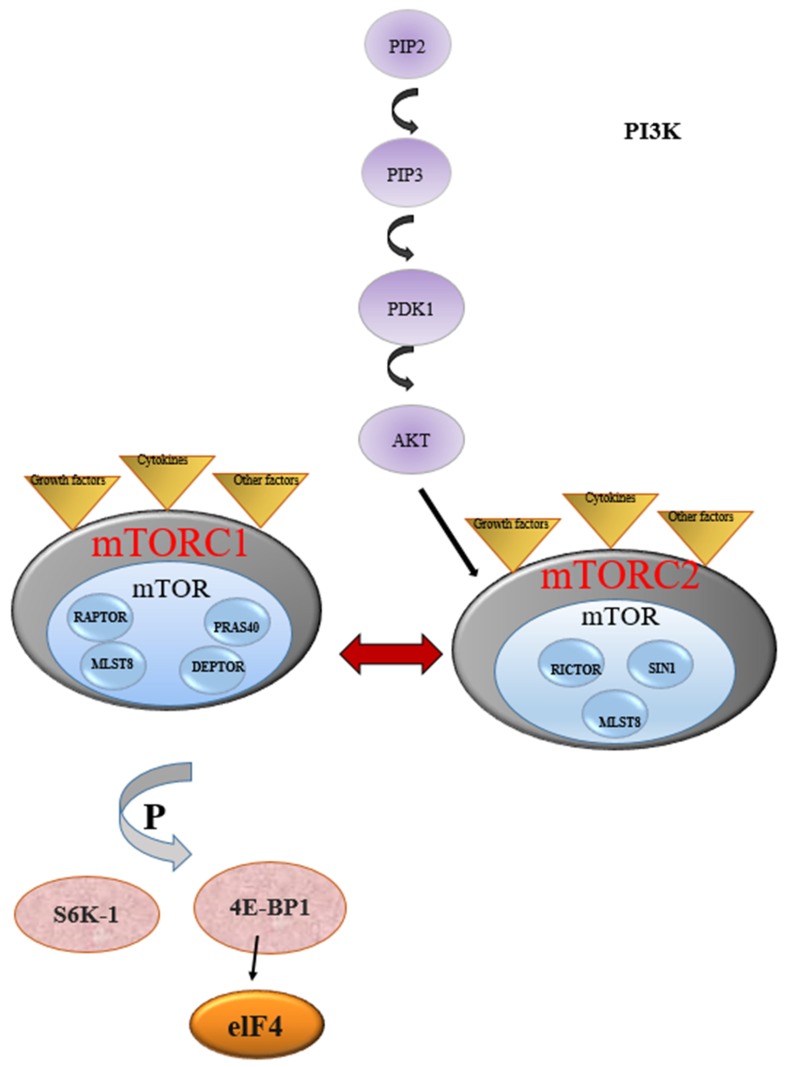
Figure 1.
The phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway. Activation of P13K phosphorylates phosphatidylinositol 4,5-biphosphate (PIP2) to form phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-triphosphate (PIP3). PIP3 prompts the activation of downstream processes such as AKT, which transmits signals to effectors including mTOR complexes to enhance cellular processes. mTORC1 is stimulated during cell activation, whereby T-cell receptor (TCR) stimulates the activation of P13K. mTORC1 includes catalytic subunits of mTOR such as regulatory-associated protein of mTOR (RAPTOR), mammalian lethal with sec-13 protein 8 (MLST8), proline-rich Akt-substrate 40 kDa (PRAS40), and DEP domain-containing mTOR-interacting protein (DEPTOR). mTORC2 comprises three proteins: RICTOR, MLST8, and SIN1. Activation of mTORC2 occurs through the phosphorylation of AKT, while mTORC1, when activated, phosphorylates effectors that are major regulators of protein translation including translation-regulating factors ribosomal S6 kinase-1 (S6K-1) and eukaryote translation initiation factor 4E binding protein-1 (4EBP1) to enhance protein synthesis.