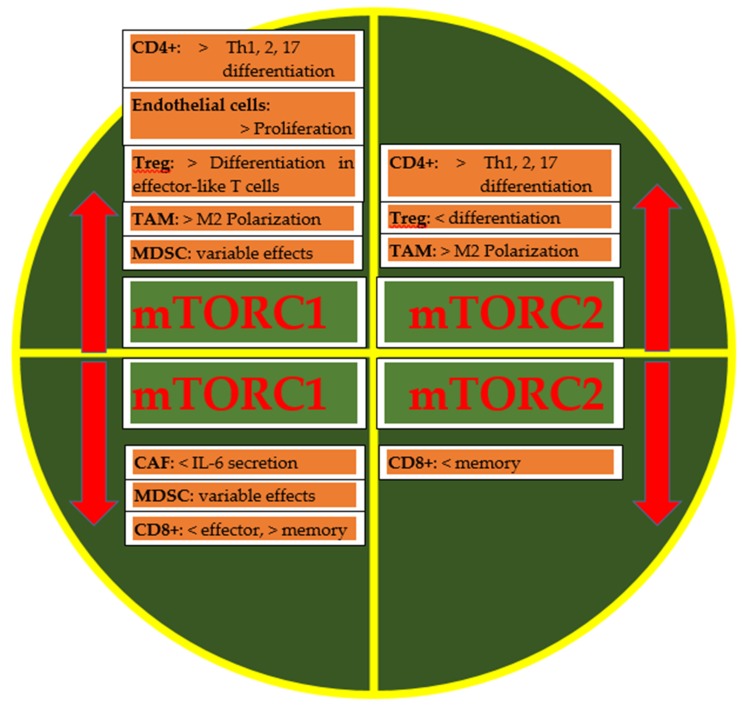
Figure 2.
Immunoregulatory functions of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) complexes in tumor microenvironment elements. An increase (red up-arrow) in mTORC1 activity induces Th1, Th2, and Th17 differentiation, endothelial proliferation, tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cells (Treg) differentiation in effector T cells, and M2 polarization; mTORC2 increased activity increases Th1, Th2, Th17 and M2 polarization and diminishes Treg differentiation; reduction (red down-arrow) of mTORC1 activity diminishes interleukin (IL)-6 production and CD8+ effector while increasing CD8+ memory; on the contrary, CD8+ memory is reduced if mTORC2 activity is diminished. mTOR complex 1: mTORC1. mTOR complex 2: mTORC2. Tumor-associated macrophages: TAM. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells: MDSCs. Cancer associated-fibroblasts: CAFs. < indicates a decrease in activity; > indicates an increase in activity.