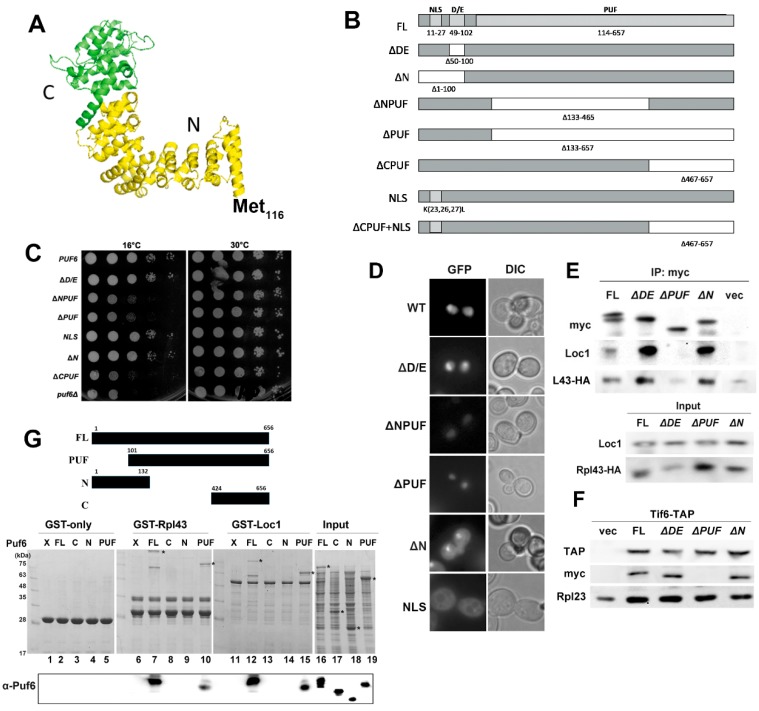
Figure 5.
Examinations of Puf6 mutants. (A) The PUF domain of Puf6. PDB (4WZR) was used as a template in protein modeling. (B) A diagram of Puf6 truncation mutants. (C) PUF6 (PKL52), ΔD/E (PKL53), ∆NPUF (PKL55), ∆PUF (PKL54), NLS (PKL199), ∆N (PKL188), ΔCPUF (PKL304), and vector were transformed to puf6Δ cells. Cells were normalized and spotted on a Leu-Glc plate with serial dilution. Plates were incubated at 16 and 30 °C. (D) The GFP localizations of various Puf6 mutants were monitored under fluorescence microscopy. (E) PUF6-myc (PKL85), puf6ΔDE-myc (PKL86), puf6ΔPUF-myc (PKL87), and puf6ΔN-myc (PKL189) were transformed to BY4741 containing RPL43-HA (PKL350). Puf6 was immunoprecipitated, and we examined the interaction with Loc1 and Rpl43. (F) Tif6-TAP was immunoprecipitated, and the interactions with Puf6 mutants were examined. (G) GST, GST-Rpl43 (PKL474), and GST-Loc1 (PKL400) interacted with Puf6 (PKL56), Puf6N (PKL662), Puf6C (PKL663), and the PUF domain (PKL512). The positions of Puf6 mutants were indicated with *.