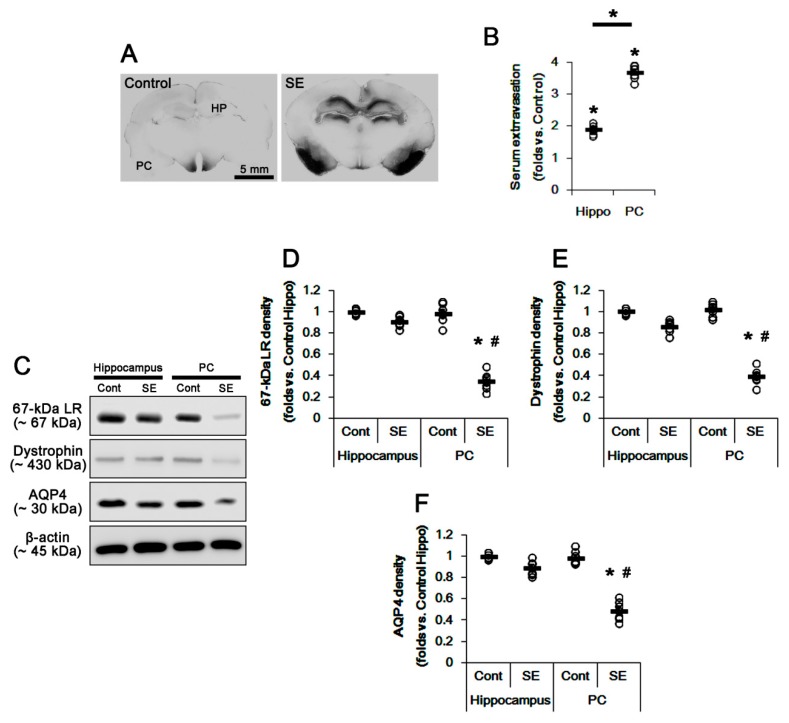
Figure 1.
Vasogenic edema formation and expressions of 67-kDa LR, dystrophin, and AQP4 in the hippocampus and the PC at 3 days after SE. SE led to serum extravasation in the PC more than the hippocampus. In addition, expressions of 67-kDa LR, dystrophin, and AQP4 were decreased in the PC, but not in the hippocampus, at 3 days after SE. (A) Representative photographs for vasogenic edema in the hippocampus and the PC using immunohistochemistry for anti-rat IgG. (B) Quantitative values (mean ± S.E.M) of the serum extravasation in the hippocampus and the PC at 3 days after SE (n = 7, respectively). Open circles indicate each value. Horizontal bars indicate the mean value. Significant differences are * p < 0.05 vs. control animals and hippocampus (unpaired and paired Student’s t-test). (C) Representative western blot images for 67-kDa LR, dystrophin, and AQP4 in the hippocampus and the PC. (D–F) Quantitative values (mean ± S.E.M) of the western blot data concerning expression levels of 67-kDa LR (D), dystrophin (E), and AQP4 (F) at 3 days after SE (n = 7, respectively). Open circles indicate each value. Horizontal bars indicate the mean value. Significant differences are *,# p < 0.05 vs. control animals and hippocampus (two-way ANOVA followed by Newman–Keuls posthoc test). LR: laminin receptor, AQP4: aquaporin 4, SE: status epilepticus, PC: piriform cortex.