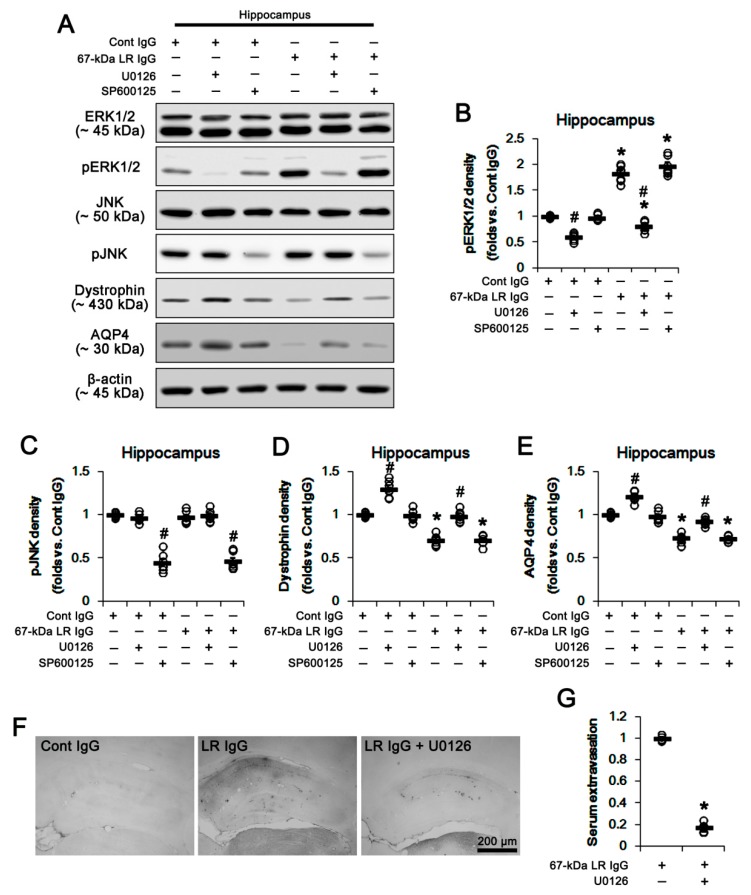
Figure 7.
Effects of 67-kDa LR (LR) neutralization on ERK1/2 and JNK activities in the hippocampus of normal animals. U0126 (an ERK1/2 inhibitor), but not SP600125 (a JNK inhibitor), increased expressions of dystrophin and AQP4 in the hippocampus of control IgG-infused animals. The 67-kDa LR IgG infusion elevated pERK1/2, but reduced expressions of dystrophin and AQP4 in the hippocampus, which were attenuated by U0126. SP600125 (a JNK inhibitor) decreased only JNK phosphorylation. U0126 also mitigated vasogenic edema induced by 67-kDa LR neutralization. (A) Western blot image for expression and phosphorylation levels of ERK1/2, JNK, dystrophin, and AQP4. (B–E) Quantitative values (mean ± S.E.M) of the western blot data concerning phosphorylation and expression levels of ERK1/2 (B), JNK (C), dystrophin (D), and AQP4 (E) (n = 7, respectively). Open circles indicate each value. Horizontal bars indicate the mean value. Significant differences are *,# p < 0.05 vs. control IgG and vehicle, respectively (one-way ANOVA followed by Newman–Keuls posthoc test). (F) Representative photographs for serum extravasation in the hippocampus induced by 67-kDa LR neutralization. (G) Quantitative values (mean ± S.E.M) of the serum extravasation in the hippocampus (n = 7, respectively). Open circles indicate each value. Horizontal bars indicate the mean value. Significant differences are * p < 0.05 vs. 67-kDa LR IgG (unpaired Student’s t-test). ERK1/2: extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2, JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase.