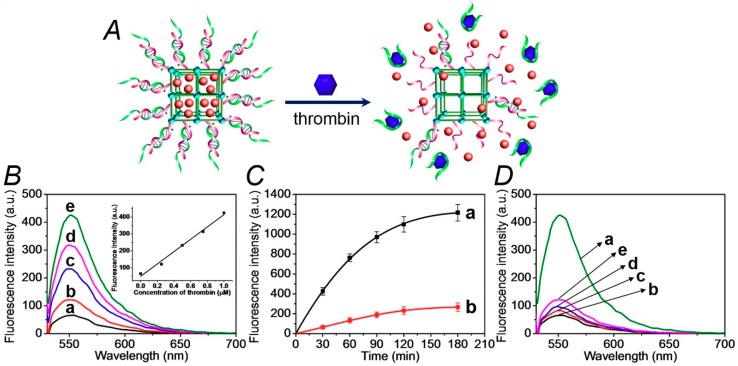
Figure 2.
(A) Schematic unlocking of the (1)/(2)-gated NMOFs and the release of rhodamine 6G, in the presence of thrombin, via the separation of the duplex gates by the formation of aptamer/thrombin complexes. (B) Fluorescence spectra of the released rhodamine 6G from the dye-loaded NMOFs upon treatment with variable concentrations of thrombin for a fixed time-interval of 30 minutes: (a) 0 μM, (b) 0.25 μM, (c) 0.5 μM, (d) 0.75 μM, and (e) 1.0 μM. Inset: the calibration curve of the released rhodamine 6G upon treatment with different concentrations of thrombin. (C) Time-dependent fluorescence changes upon the release of rhodamine 6G from the (1)/(2)-gated dye-loaded NMOFs in the presence of: (a) thrombin, 1 μM, (b) No thrombin added. (D) Fluorescence spectra of rhodamine 6G released from the (1)/(2)-gated, dye-loaded, NMOFs upon treatment for a fixed time interval corresponding to 30 minutes with: (a) thrombin, 1 μM, (b) no thrombin added, (c) bovine serum albumin (BSA), 1 μM, (d) hemoglobin, 1 μM, (e) vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), 1 μM. The binding of the thrombin to the aptamer units and all the release experiments were performed in the HEPES buffer solution, 10 mM, pH = 7.4, containing 20 mM of NaCl, 10 mM of KCl, and 10 mM of MgCl2.