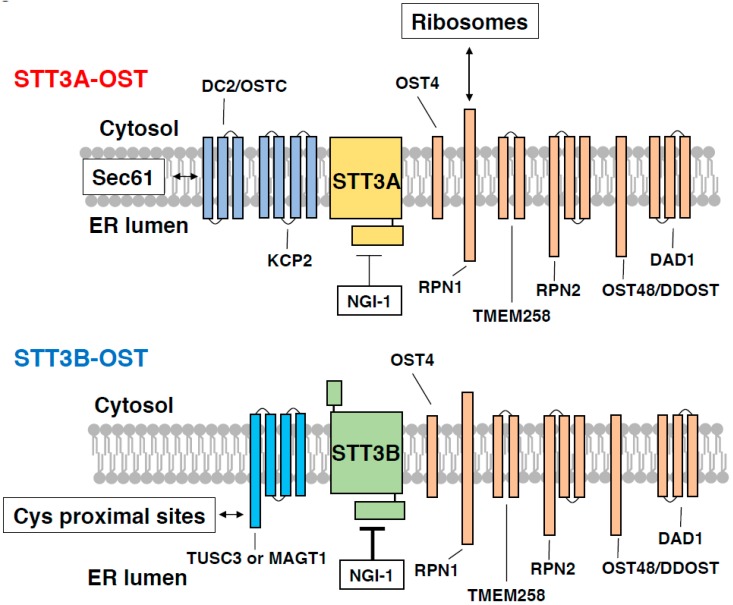
Figure 2.
Subunit composition of STT3A-OST and STT3B-OST. STT3A-OST (upper side) and STT3B-OST (lower side) contain six shared subunits (RPN1, RPN2, DAD1, OST48, OST4, and TMEM258; shown in orange) and specific subunits (DC2/OSTC and KCP2 for STT3A-OST; shown in dark blue, and TUSC3 and MAGT1 for STT3B-OST; shown in cyan). The cytosolic domain of RPN1 in complex with STT3A-OST makes contact with the 60S subunit of membrane-bound ribosomes [35]. In contrast, DC2/OSTC mediates interaction between STT3A-OST and Sec61 protein-conducting channel [35], allowing co-translational N-glycosylation. STT3B-OST contains either one of TUSC3 or MAGT1, which has an oxidoreductase activity and facilitates N-glycosylation of Cys proximal sites [33]. N-glycosylation inhibitor 1 (NGI-1) inhibits STT3B-OST more efficiently than STT3A-OST (represented by thick and thin T bars) [43].